Picture |
Object
name
#NORAD |
Description |
Launch
Date |
Weight |


|
DMSP
F-19
DMSP 5D-3/F19
USA249
#39640
(2014-015A) |
DMSP-F19, also known
as DMSP 5D-3 F19 or USA 249, is a US Department of Defense
weather satellite launched on an Atlas 5 rocket from
Vandenberg into a 850km high sun-synchronous orbit.
DMSP
is a space- and ground-based system used to collect
and disseminate timely global environmental data to
the Department of Defense and other governmental agencies.
This environmental data consists of visible and infrared
cloud cover and other specialized meteorological, oceanographic,
and solar-geophysical information required to support
the war fighter. DMSP satellites “see” environmental
features such as clouds, bodies of water, snow, fire,
and pollution in the visual and infrared spectra. The
data can be used to determine cloud type and height,
land and surface water temperatures, water currents,
ocean surface features, ice, and snow. DMSP data are
processed on the ground, interpreted by meteorologists,
and ultimately used in planning and conducting U.S.
military operations worldwide. |
Apr
3rd 2014 |
1200
kg |
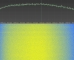 The
S-Band wideband downlink on 2252.5 MHz of DMSP F-18
was received and enclosed FFT plot was generated in
May 2014 by Milen Rangelov. The
S-Band wideband downlink on 2252.5 MHz of DMSP F-18
was received and enclosed FFT plot was generated in
May 2014 by Milen Rangelov.
|


|
Sentinel-1
Sentinel-1A
#39643
(2014-016A) |
Sentinel-1
is a Earth Observation satellite built by Thales Alenia
Space for ESA. I features a synthetic aperture radar
(SAR) operating in C-Band (5.405 GHz, 90 MHz bandwidth)
and expected to provide a ground resolution of down
to 0.5m. it is the first of a series of 5 satellites
and part of GMES (Global Monitoring for Environment
and Security) program of the European Union. In 2012
GMES was renamed to Copernicus.
Its downlinks are:
S-Band 2254.1 MHz, 2.2 MHz bandwidth
X-Band channel
1: 8095 MHZ, 140 MHz bandwidth
X-Band channel 2:
8260 MHz , 140 MHz bandwidth
The uplink is:
S-Band 2075.6504 MHz, 768 kHz bandwidth
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
April 4th
2014 |
2280 kg |

|
SporeSat
#39681
(2014-022B) |
SporeSat
is an autonomous, free-flying three-unit (3U) spacecraft
that will be used to conduct scientific experiments
to gain a deeper knowledge of the mechanisms of plant
cell gravity sensing. SporeSat was launched with the
falcon 9 rocket as secondary payload of SPACE-X CRS-3.
The 3U Cubesat was built by NASA Ames Research Center,
Santa Clara University, Purdue University, and University
of Texas. It will transmit every 5 seconds an AX-25
packet on 437.100 MHz.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
April 18th
2014 |
5 kg |

|
TSAT
#39682
(2014-022C) |
TSAT is a
dual mission using the GlobalStar satellite communication
modem to demonstrate a reliable and global nanosat network
and a Space Weather bus design consisting of a plasma
probe, 3-axis magnetometer, and 3 ultraviolet photodiodes.The
Space Weather bus will investigate the low-altitude
ionosphere (120-350 km) in the Extremely Low Earth Orbit
(ELEO) satellite region. TSAT was launched with the
falcon 9 rocket as secondary payload of SPACE-X. The
2U Cubesat was built by Taylor University.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
April 18th
2014 |
2 kg |

|
PhoneSat-v2.5
#39683
(2014-022D) |
PhoneSat-v2.5 was launched
with the falcon 9 rocket as secondary payload of SPACE-X.
The 1U Cubesat was built by NASA Ames Research Center.
PhoneSat 2.5 transmits on 437.425 MHz an 1200bd AFSK
beacon signal every 30 seconds when in operational mode
respectively every 150 seconds when in charging mode. |
April
18th 2014 |
1
kg |
 Mike
DK3WN received the 1200bd AFSK signal of PhoneSat-v2.5
on May 9th 2014 at 09:14 UTC.
Recording kindly provided by Mike DK3WN. Mike
DK3WN received the 1200bd AFSK signal of PhoneSat-v2.5
on May 9th 2014 at 09:14 UTC.
Recording kindly provided by Mike DK3WN.
|

|
ALL-STAR/THEIA
#39684
(2014-022E) |
THEIA is
an imaging payload built to test the capabilities of
the ALLSTAR-1 Bus. ALL-STAR/THEIA was launched with
the falcon 9 rocket as secondary payload of SPACE-X.
The 3U Cubesat was built by Colorado Space Grant Consortium
at the University of Colorado at Boulder. ALL-STAR features
a S-Band downlink at 2.4017 GHz transmitting a 254kbps
BPSK signal every 15 seconds.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
April 18th
2014 |
4 kg |

|
Kick
Sat
#39685
(2014-022F) |
Kick Sat was launched
with the falcon 9 rocket as secondary payload of SPACE-X.
The 3U Cubesat was built by Cornell University. The
mothership transmits a beacon at 437.505 MHz with 1200
Baud AFSK (AD.25 packets). It was supposed to deploy
more than 100 small ChipSats (Sprites) which should
transmit on 447.240 MHz using a proprietary protocol.
However the deployment did not work. KickSat decayed
on May 14th 2014. |
April
18th 2014 |
5.5
kg |
  On April 22nd 2014 at 00:00
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 1200bd packet radio signal
of Kicksat on 437.505 MHz. Recording and waterfall plot
kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On April 22nd 2014 at 00:00
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 1200bd packet radio signal
of Kicksat on 437.505 MHz. Recording and waterfall plot
kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|

|
COSMOS
2499
KOSMOS 2499
RS-47
#39765
(2014-028E) |
KOSMOS 2499 is a Russian
military satellite. It was launched on May 23rd
2014 at 22:54 UTC from Plesetsk, Russia on a Soyuz-2.1b
rocket.
After its launch COSMOS-2499 made a number
of orbital changes.
End of 2014 it was reported
by Dmitry Pashkov R4UAB that this satellite also carries
RS-47 operating at 435.465 MHz and 435.565 MHz. On November
30th 2014 the satellite started
identifying itself in morse code on 435.465 MHz as RS-47. |
May
23rd 2014 |
48-100
kg |
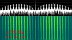 On
Dec. 2nd 2014 Paul Marsh M0EYT
from UHF-Satcom reported a successful
reception of an S-band downlink of COSMOS-2499 at 2280
MHz. Enclosed spectrum plot kindly provided by UHF-Satcom. On
Dec. 2nd 2014 Paul Marsh M0EYT
from UHF-Satcom reported a successful
reception of an S-band downlink of COSMOS-2499 at 2280
MHz. Enclosed spectrum plot kindly provided by UHF-Satcom.
|
  On
December 5th 2014 at 19:54
UTC Enrico Gobbetti IW2AGJ received 70cm downlink signal
during orbit #1515 of COSMOS-2499 on 435.572 MHz. Spectrum
plot and audio recording kindly provided by Enrico IW2AGJ. On
December 5th 2014 at 19:54
UTC Enrico Gobbetti IW2AGJ received 70cm downlink signal
during orbit #1515 of COSMOS-2499 on 435.572 MHz. Spectrum
plot and audio recording kindly provided by Enrico IW2AGJ.
|
 In the
morning of December 11th 2014
during orbit 2587 Jean-Pierre Godet received the following
CW telemetry of RS-47 on 435.465 MHz: "TCON 154 MCON
69 SMA
73 SMB
79 MRXA
26 MRXB 14
RS47 UBS 165 UAB 164 IBS 0". Audio
recording kindly provided by Jean-Pierre F5YG. In the
morning of December 11th 2014
during orbit 2587 Jean-Pierre Godet received the following
CW telemetry of RS-47 on 435.465 MHz: "TCON 154 MCON
69 SMA
73 SMB
79 MRXA
26 MRXB 14
RS47 UBS 165 UAB 164 IBS 0". Audio
recording kindly provided by Jean-Pierre F5YG.
|
 Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW downlink of RS-47 on 435.565
MHz on August 1st2015 at 18:20
UTC. Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW downlink of RS-47 on 435.565
MHz on August 1st2015 at 18:20
UTC. Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|



|
KazEOSat-2
# 40010
(2014-033A) |
KazEOSat-2
was launched as one of the 4 main payloads together
with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr rocket on
Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. Built
by Surrey Satellite Technology Limited of the United
Kingdom, KazEOSat-2 is based upon the SSTL-150+ satellite
bus and carries a camera which can image the Earth at
resolutions of up to 6.5 meter.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
185 kg |
 |
Hodoyoshi-4
#40011
(2014-033B) |
Hodoyoshi-4
was launched as one of the 4 main payloads together
with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr rocket on
Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. Hodoyoshi-4
is equipped with a single, more powerful, instrument
providing a resolution of 6 meter per pixel. Is is also
equipped for further technology demonstration, and store-and-forward
communications.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
66 kg |


|
UniSat-6
G.A.U.S.S.
#40012
(2014-033C) |
UniSat-6 was launched
together with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr
rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. Like
UniSat-5, UniSat-6 carries CubeSat dispensers however
it lacks the PocketQube deployers flown on the previous
mission. Four CubeSats are expected to be deployed from
UniSat-6 at a later date: AeroCube-6, Lemur-1, TigriSat
and Antelsat. UniSat-6 features a 9600bd
downlink at 437.425 MHz. |
June
19th 2014 |
26
kg |
  On July 20th 2014 at 09:16
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 9600bd packet radio signal
of UniSat-6 on 437.425 MHz. Recording and waterfall
plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On July 20th 2014 at 09:16
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 9600bd packet radio signal
of UniSat-6 on 437.425 MHz. Recording and waterfall
plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|
  On
July 27th 2014 at 09:22 UTC
the G.A.U.S.S-team switched the satellite to a low resolution
mode of 160px. Thus they were able to create a picture
every 1.1 seconds and downlink a series of pictures
while passing over Europe. They combined the pictures
and compiled enclosed video which is running at 2x the
original speed. You can see in the video the Earth passing
by the camera while the satellite is spinning once around
every 10 seconds. Audio recording of the data downlink
and video kindly provided by Aitor Conde from the G.A.U.S.S.
team. On
July 27th 2014 at 09:22 UTC
the G.A.U.S.S-team switched the satellite to a low resolution
mode of 160px. Thus they were able to create a picture
every 1.1 seconds and downlink a series of pictures
while passing over Europe. They combined the pictures
and compiled enclosed video which is running at 2x the
original speed. You can see in the video the Earth passing
by the camera while the satellite is spinning once around
every 10 seconds. Audio recording of the data downlink
and video kindly provided by Aitor Conde from the G.A.U.S.S.
team.
|


|
Deimos-2
#40013
(2014-033D) |
Deimos-2
was launched as one of the 4 main payloads together
with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr rocket on
Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. It
will be used for high-resolution Earth imaging; it’s
EOS-D imager is capable of producing pictures at resolutions
as high as 0.75 meter.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
300
kg |
 |
BugSat-1
TITA
#40014
(2014-033E) |
BugSat-1 was launched
together with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr
rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. It
was built by Satellogic. They have been part of the
team who built also CubeBug-1 and CubeBug-2. Besides
a C-Band downlink it also features a 9600Bd GMSK AX.25
downlink on 437.445 MHz. |
June
19th 2014 |
25
kg |
On January 5th
2015 at 22:46 UTC Darko
9A3LI, reported the following reception
on 437.450 MHz in 9600bd FSK AX25 KISS mode:
EMAIL
:tita@satellogic.com ..Upt: 04:29:30
......Bat:12.22v ..Temp:24.1C ..Gyr:0.99d/s ..
It
is most likely that this signal was sent from BugSat-1
as the satellite was over his area at that time too. |
 On March
22nd 2015 Francisco EA7ADI
received the 9600bd FSK downlink of BugSat-1. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On March
22nd 2015 Francisco EA7ADI
received the 9600bd FSK downlink of BugSat-1. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 On May
1st 2015 at 10:08 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9600bd FSK downlink of BugSat-1.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On May
1st 2015 at 10:08 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9600bd FSK downlink of BugSat-1.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 |
Hodoyoshi-3
#40015
(2014-033F) |
Hodoyoshi-3
was launched as one of the 4 main payloads together
with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr rocket on
Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. Hodoyoshi-3
carries two cameras with resolutions of 40 and 200 meter
per pixel. Is is also equipped for further technology
demonstration, and store-and-forward communications.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
60 kg |


|
SaudiSat-4
#40016
(2014-033G) |
SaudiSat-4
was launched together with 36 other satellites on a
Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. SaudiSat-4
spacecraft will be used to study whether a phenomenon
called the photoelectric effect, which causes metals
to emit electrons when exposed to ultraviolet radiation,
can be use to cancel out electrical charges which build
up in satellite components over time.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
100 kg |

 |
TabletSat-Aurora
TabletSat-2U-EO
#40017
(2014-033H) |
TabletSat-Aurora
was designed and built by Russian startup company SPUTNUK.
It was launched together with 36 other satellites on
a Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. This
satellite is a technology demonstrator amd will observe
the Earth, returning images with a resolution of up
to 15 meter.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 19th
2014 |
25 kg |
 |
AprizeSat-9
#40018
(2014-033J) |
AprizeSat-9
was launched together with 36 other satellites on a
Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. AprizeSat-9
will be used for commercial communications.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
12 kg |
 |
AprizeSat-10
#40019
(2014-033K) |
AprizeSat-10
was launched together with 36 other satellites on a
Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. AprizeSat-10
will be used for commercial communications.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
12 kg |
 |
BRITE-Toronto
BRITE-CA 1
#40020
(2014-033L) |
BRITE-Toronto
was launched together with 36 other satellites on a
Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. BRITE-CA
1 is the fourth member of the six-satellite Bright Star
Target Explorer (BRITE) constellation.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June
19th 2014 |
10
kg |


|
Duchifat-1
DUCHIFAT-1
#40021
(2014-033M ) |
Duchifat-1 was launched
together with 36 other satellites on a Russian
Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. The
Israeli satellite was being developed as part of a special
QB50 project for students, who are building special-purpose
cubesats for a variety of purposes. Duchifat-1 responds
to APRS signals and can be used to locate lost travelers.
The 1200bd BPSK downlink is on 145.980 MHz. |
June
19th 2014 |
0,86
kg |
  On July 20th 2014 at 22:15
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 1200bd BPSK packet radio
signal of Duchifat-1 on 145.980 MHz. Recording and waterfall
plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On July 20th 2014 at 22:15
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 1200bd BPSK packet radio
signal of Duchifat-1 on 145.980 MHz. Recording and waterfall
plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|
 |
PACE
#40023
(2014-033P) |
Platform
for Attitude Control Experiments (PACE) CubeSat was
launched together with 36 other satellites on a Russian
Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia.
No signal reports were received after
its launch. |
June 19th
2014 |
2
kg |


|
NanoSatC-Br 1
#40024
(2014-033Q) |
NanoSatC-Br 1 was
launched together with 36 other satellites on a Russian
Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. It
features a 1200bd BPSK downlink at 145.865 MHz. |
June
19th 2014 |
1
kg |
 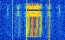 On July 20th 2014 at 08:53
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 1200bd BPSK packet radio
signal of NanoSatC-Br 1 on 145.865 MHz. Recording and
waterfall plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On July 20th 2014 at 08:53
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 1200bd BPSK packet radio
signal of NanoSatC-Br 1 on 145.865 MHz. Recording and
waterfall plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|
 On December
13th 2014 Francisco EA7ADI
received the CW downlink of NanoSatC-BR1. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On December
13th 2014 Francisco EA7ADI
received the CW downlink of NanoSatC-BR1. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 |
POPSAT-HIP-1
#40028
(2014-033U) |
POPSAT-HIP-1 is
a 3-unit cubesat built
by Microspace Rapid Pte Ltd., Singapore and launched
together with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr
rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. The
satellite shall demonstrate the functionality of a high
resolution optical payload and attitude control micropropulsion
propulsion system on a Cubesat Class Nano-satellite.
POPSAT-HIP1 transmits on 437.405 MHz with 2 Watts in
CW, 1200bd AFSK and 9600bd FSK CCSDS. |
June
19th 2014 |
3
kg |
 Enclosed
recording of the CW downlink signal of POPSAT-HIP1 was
kindly provided by Giulio IV3DTB/9V1FC
. Enclosed
recording of the CW downlink signal of POPSAT-HIP1 was
kindly provided by Giulio IV3DTB/9V1FC
.
|
 On December
31st 2014 at 10:30 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW signal of POPSAT-HIP-1. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On December
31st 2014 at 10:30 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW signal of POPSAT-HIP-1. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 |
DTUSat-2
OZ2DTU
#40030
(2014-033W) |
DTUSat-2 (Danish
Technical University Satellite-2) was launched together
with 36 other satellites on a Russian Dnepr rocket on
Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. Its
primary mission is bird migration monitoring and tracking.
The uplink is at
1268.900 MHz in 9.6kbit/s CPFSK modulation.
The downlink is
at 2401.835 MHz (some have reported 2401.842 MHz) with
an output power up to 220mWand features several modes:
A CW beacon (30 bit/s OOK) with 220mW output power using
the callsign OZ2DTU is repeated ever 30 or 60 seconds
(depending on OBC is running or not ). Alternatively
the downlink can be switched also to transmit data in
1.2kbit/s, 19.2kbit/s and 38.4kbit/s MSK modulation.
|
June
19th 2014 |
1
kg |
  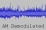 Enclosed
CW and MSK signal was received on August 28th
2015 at 09:27:40 UTC on 2401.840 MHz by DD1US. Enclosed
CW and MSK signal was received on August 28th
2015 at 09:27:40 UTC on 2401.840 MHz by DD1US.  One
can clearly hear the beacon transmiting ?Z2DTU followed
by the bits 100100100.Finally a short MSK transmission. One
can clearly hear the beacon transmiting ?Z2DTU followed
by the bits 100100100.Finally a short MSK transmission.
 The
signals were demodulated in AM and FM because CW is
best audible in AM whereas MSK is audible only using
an FM demodulator. The
signals were demodulated in AM and FM because CW is
best audible in AM whereas MSK is audible only using
an FM demodulator.
|


|
AntelSat
#40034
(2014-033AA) |
AntelSat was released
by UniSat-6 25 hours and 38 minutes after separation
from the launch vehicle. The launch was on a Russian
Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. |
June
19th 2014 |
2
kg |
 Mike
DK3WN received the 1200bd AFSK signal of AntelSat on
March 30th 2015 at 08:43 UTC.
Recording kindly provided by Mike DK3WN. Mike
DK3WN received the 1200bd AFSK signal of AntelSat on
March 30th 2015 at 08:43 UTC.
Recording kindly provided by Mike DK3WN.
|
 |
Perseus-M 2
#40037
(2014-033AD) |
Perseus-M 2 was
launched together with 36 other satellites on a Russian
Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. It is the second
6-unit cubesat and carries an AIS receiver intended
to collect data on the position and status of ships
at sea. |
June
19th 2014 |
|
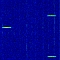  On March
23rd 2015 at 22:33 UTC Darko
9A3LI, received on 400.167 MHz the signals
of Perseus-M1 and Perseus-M2. Enclosed spectrum plot
and audio recording which contains the signals of both,
Perseus-M1 and M2 were kindly provided by Darko 9A3LI. On March
23rd 2015 at 22:33 UTC Darko
9A3LI, received on 400.167 MHz the signals
of Perseus-M1 and Perseus-M2. Enclosed spectrum plot
and audio recording which contains the signals of both,
Perseus-M1 and M2 were kindly provided by Darko 9A3LI.
|
 |
Perseus-M 1
#40039
(2014-033AF) |
Perseus-M 1 was
launched together with 36 other satellites on a Russian
Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. Its is the first
6-unit cubesat and carries an AIS receiver intended
to collect data on the position and status of ships
at sea. |
June
19th 2014 |
|
  On March
23rd 2015 at 22:33 UTC Darko 9A3LI, received on 400.167
MHz the signals of Perseus-M1 and Perseus-M2. Enclosed
spectrum plot and audio recording which contains the
signals of both, Perseus-M1 and M2 were kindly provided
by Darko 9A3LI. On March
23rd 2015 at 22:33 UTC Darko 9A3LI, received on 400.167
MHz the signals of Perseus-M1 and Perseus-M2. Enclosed
spectrum plot and audio recording which contains the
signals of both, Perseus-M1 and M2 were kindly provided
by Darko 9A3LI.
|

|
PolyITAN-1
#40042
(2014-033AJ) |
PolyITAN-1 is a
CubeSat designed and built by the National Technical
University of Ukraine – KPI in cooperation with the
Ukrainian HAM radio community. The mission is to launch
Ukrainian educational satellite build by KPI students
and space exploration enthusiasts. PolyITAN-1
was launched together with 36 other satellites
on a Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th
2014 at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia.
PolyITAN-1's
mission targets are:
- Develop, build,
test, launch and operate a Ukrainian small satellite
platform based on Cubesat standard.
- Conduct
mission experiments with following payloads: Sun sensor,
attitude position and orientation system including system
software and test on-board GLONASS/GPS navigation subsystem.
- Build
ground segment infrastructure for satellite communication.
- Develop
and test onboard and ground telecommunication software,
implement telecommunication protocols.
- Establish
cooperation between educational institute, space agency(s)
and various government authorities, HAM radio community
and others.
PolyITAN-1 features a 1200bd AFSK/CW
downlink on 437.675 MHz. It uses the callsign EM0UKPI. |
June
19th 2014 |
1
kg |
 On December
14th 2014 at 12:01 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the AFSK downlink signal of PolyITAN-1.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On December
14th 2014 at 12:01 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the AFSK downlink signal of PolyITAN-1.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 |
TigriSat
#40043
(2014-033AK) |
TigriSat, Irak's
first cubeat, was released by UniSat-6 25 hours and
38 minutes after separation from the launch vehicle.
The launch was on a Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday,
June 19th 2014 at 19:11h
UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. The
9600 bd downlink is on 435.000 MHz. |
June
19th 2014 |
3
kg |
  On July 20th 2014 at 22:25
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 9600bd packet radio signal
of TigriSat on 435.000 MHz. Recording and waterfall
plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On July 20th 2014 at 22:25
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the 9600bd packet radio signal
of TigriSat on 435.000 MHz. Recording and waterfall
plot kindly provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|
 On May
1st 2015 at 09:46 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9600bd FSK downlink of TirgriSat.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On May
1st 2015 at 09:46 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9600bd FSK downlink of TirgriSat.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 |
Lemur-1
#40044
(2014-033AL) |
Lemus-1
was released by UniSat-6 25 hours and 38 minutes after
separation from the launch vehicle. The launch was on
a Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 19th
2014 |
4
kg |
 |
AeroCube-6A
AC 6A
#40045
(2014-033AM) |
AeroCube
6 was released by UniSat-6 25 hours and 38 minutes after
separation from the launch vehicle. The launch was on
a Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. After
release of AeroCube 6 by UniSat-6 it separate34d
in a
pair of nano-satellites. The payload of the
two spin-stabilized sun-pointing 0.5U cubesats consists
of miniaturized dosimeters, an inter-satellite cross-link
experiment, an integrated flight computer, a GPS receiver,
an UHF transceiver board and new attitude sensors.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 19th
2014 |
0,5
kg |
 |
AeroCube-6B
AC 6B
#40046
(2014-033AN) |
AeroCube
6 was released by UniSat-6 25 hours and 38 minutes after
separation from the launch vehicle. The launch was on
a Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia. After
release of AeroCube 6 by UniSat-6 it separate34d
in a
pair of nano-satellites. The payload of the
two spin-stabilized sun-pointing 0.5U cubesats consists
of miniaturized dosimeters, an inter-satellite cross-link
experiment, an integrated flight computer, a GPS receiver,
an UHF transceiver board and new attitude sensors.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 19th
2014 |
0,5
kg |
 |
BRITE-Montreal
BRITE-CA 2
#40047
(2014-033AP) |
BRITE-Montreal
was launched together with 36 other satellites on a
Russian Dnepr rocket on Thursday, June 19th 2014
at 19:11h UTC from Dombarovsky in Southern Russia.
BRITE-CA 2 is the fifth member of the six-satellite
Bright Star Target Explorer (BRITE) constellation. BRITE-CA
2 (BRITE-Montreal) failed to separate from the launch
vehicle and thus no signals were received. |
June
19th 2014 |
10
kg |



|
SPOT
7
Azersky
#40053
(2014-034A) |
SPOT
7 (Satellite Probatoire de l'Observation de la Terre)
is an agile Earth observation satellite. It offers 2
meter resolution data in a 60 kilometer by 60 kilometer
swath. The satellite features two NAOMI (New AstroSat
Optical Modular Instrument) instruments. SPOT
7 was successfully launched on June 30th
2014 on an Indian PSLV-CA rocket. After successful launch
and initial operation the satellite was sold to Azerbaijan's
space agency Azercosmos and renamed Azersky.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 30th
2014 |
712 kg |



|
AISat 1
#40054
(2014-034B) |
AISat
1 is an German microsatellite, which carries an experimental
spacecraft-based Automatic Identification System (AIS)
sensor in low-Earth orbit as a means of tracking maritime
assets. AISat 1 was successfully launched
on June 30th 2014 on an Indian
PSLV-CA rocket.
The satellite is
based on DLR's experimental CLAVIS platform. The cube-shaped
satellite body carries solar cells for power generation.
AISat 1 is carrying an experimental AIS receiver with
a 4 m long helix antenna that also forms a gravity gradient
boom. This high gain antenna enables the satellite to
receive Class-A and Class-B AIS signals as well as the
AIS-SART (AIS Search and Rescue Transmitter) signals.
AISat-1 uses downlink frequencies of 437.250
MHz and 437.511 MHz. The callsign used is DP0AIS. |
June
30th 2014 |
14
kg |
  On July 19th 2014 at 20:40
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the CW signal of AISat-1
on 437.511 MHz. Recording and waterfall plot kindly
provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On July 19th 2014 at 20:40
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the CW signal of AISat-1
on 437.511 MHz. Recording and waterfall plot kindly
provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|
 On August
12th 2024 at 11:12h UTC Igor
PU4ELT received the CW beacon of DP0AIS on 437.513 MHz
. Recording kindly provided by Igor PU4ELT. On August
12th 2024 at 11:12h UTC Igor
PU4ELT received the CW beacon of DP0AIS on 437.513 MHz
. Recording kindly provided by Igor PU4ELT.
|

|
CanX-4
#40055
(2014-034C) |
CanX-4
and CanX-5 (Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiments)
are a pair of identical nanosatellites. They
were successfully launched on June 30th
2014 on an Indian PSLV-CA rocket. Their primary mission
is the demonstration of on-orbit formation flying, which
means that they are controlling their position and orientation
with respect to one another to achieve a predefined
configuration necessary for coordinated operations.
Formation will be controlled with the second generation
Nanosatellite Propulsion System (NANOPS) being developed
at UTIAS/SFL. To enable autonomous control, CanX-4/-5
employ innovative carrier-phase differential GPS techniques
to obtain relative position measurements accurate to
less than 10 cm. CanX-4 and CanX-5 will coordinate their
operations using an SFL-developed inter-satellite communication
link.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 30th
2014 |
7 kg |

|
CanX-5
#40056
(2014-034D) |
CanX-4
and CanX-5 (Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiments)
are a pair of identical nanosatellites. They
were successfully launched on June 30th
2014 on an Indian PSLV-CA rocket. Their primary mission
is the demonstration of on-orbit formation flying, which
means that they are controlling their position and orientation
with respect to one another to achieve a predefined
configuration necessary for coordinated operations.
Formation will be controlled with the second generation
Nanosatellite Propulsion System (NANOPS) being developed
at UTIAS/SFL. To enable autonomous control, CanX-4/-5
employ innovative carrier-phase differential GPS techniques
to obtain relative position measurements accurate to
less than 10 cm. CanX-4 and CanX-5 will coordinate their
operations using an SFL-developed inter-satellite communication
link.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
June 30th
2014 |
7 kg |


|
VELOX-1
#40057
(2014-034E)
VELOX-1-NSAT
#40057
(2014-034E)
&
VELOX-1-PSAT |
The
VELOX-I mission is a Singaporean nanosatellite mission
consisting of two satellites - VELOX-1-NSAT and the
VELOX-1-PSAT subsatellite - to operate in sun synchronous
Low Earth’s Orbit (LEO). The project is part of NTU’s
Undergraduate Satellite Program, which provides an opportunity
for engineering students to participate in a multidisciplinary
hands-on space project and to conduct several
technology demonstrations. VELOX-1 was
successfully launched on June 30th
2014 on an Indian PSLV-CA rocket.
The mission objectives
are:
- To
launch a nanosatellite, which is designed, built, and
operated by students from different schools in the College
of Engineering, NTU.
- To acquire images
of Earth and transmit them back to ground station using
a narrow angle camera with tele-optics to provide high-resolution
images of Earth from LEO.
- To provide technology
demonstration of several payloads like a vision system,
a dual-FOV sun sensor and a quantum physics payload.
- To
separate into a nanosatellite (N-Sat) and a picosatellite
(P-Sat) for intersatellite communication experiment.
VELOX-1-NSAT is
a 3U CubeSat, which deploys the VELOX-1-PSAT subsatellite
in orbit. NSAT features four deployable solar arrays
and has a projected life time of 2 years. The payload
consists of a imaging system with extended optics for
20 m ground resolution, a quantum physics payload and
an inter-satellite communications payload.
The objective of
VELOX-1-PSAT
is to separate from the nanosatellite (N-Sat) for an
intersatellite communication experiment. PSAT
is a 0.25 kg satellite with dimensions of 60 mm ×
70 mm × 30 mm and boxy mounted solar cells. It
has a projected life time of 1 year.
VELOX-1 uses a
downlink frequency of 145.980 MHz. |
June
30th 2014 |
4,5
kg |
  On July 19th 2014 at 09:25
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the CW signal of VELOX-1
on 145.980 MHz. Recording and decoded telemetry kindly
provided by Davide IW0HLG.
On July 19th 2014 at 09:25
UTC Davide IW0HLG received the CW signal of VELOX-1
on 145.980 MHz. Recording and decoded telemetry kindly
provided by Davide IW0HLG.
|

|
Meteor-M
2
Meteor-M N2
#40069
(2014-037A) |
The Meteor-M2 weather
satellite based on VNIIEM’s Resurs-UKP, a versatile
space platform suitable for a wide range of missions.
Meteor-M2’s payloads are:
- Low
resolution multizone weather scanner (MSU-MR) for wide
swath imaging;
- Multizone
imaging complex (KMSS) for optical environment monitoring;
- Severyanin-M
X-band radar (BRLK) to obtain radar images in any weather;
- Microwave
radiometer for atmospheric temperature and humidity
sensing (MTVZA);
- Fourier infrared
spectrometer (IKFS-2);
- Heliogeophysical
complex (GGAK-M) of five instruments for global heliogeophysical
monitoring;
- Data
collection and transmission system (SSPD), including
a system to receive weather data from ground measurement
stations.
Meteor-M N2 is switching
its downlink transmitting LRPT pictures in 72 kbps between
137.100 MHz and 137.900
MHz.
1. The satellite
is in a commissioning phase and some tests are still
in progress until Nov 9th 2014.
It is planned that LRPT transmission will be declared
operational on Nov 10th 2014.
2. In operational
mode the following channels will be available:
-
channel 1 (0.5 . 0.7 µm; APID64),
- channel
2 (0,7 .1,1 µm; APID65),
- channel 5 (10,5
. µm; APID68).
3. No channel
switch is planned at the terminator line crossing, so
there will be no data in visible channels 1 and 2 during
the nighttime. |
July
8th 2014 |
2700
kg |
  On
August 4th 2014 at 09:04 UTC
Fer Paglia IW1DTU received Meteor-M N2 on 137.910 MHz.
Enclosed I/Q wav recording (41 MByte large !) was kindly
provided by Fer IW1DTU. On
August 4th 2014 at 09:04 UTC
Fer Paglia IW1DTU received Meteor-M N2 on 137.910 MHz.
Enclosed I/Q wav recording (41 MByte large !) was kindly
provided by Fer IW1DTU.
|
  On
August 18th 2014 at 07:45 UTC
Enrico Gobbetti IW2AGJ received the LRPT transmission
during orbit #576 of Meteor-M N2 on 137.100 MHz. Spectrum
plot and audio recording kindly provided by Enrico IW2AGJ. On
August 18th 2014 at 07:45 UTC
Enrico Gobbetti IW2AGJ received the LRPT transmission
during orbit #576 of Meteor-M N2 on 137.100 MHz. Spectrum
plot and audio recording kindly provided by Enrico IW2AGJ.
 Enclosed
very nice LRPT picture of Europe was received by Enrico
IW2AGJ from Meteor-M N2 during its orbit #1656 on November
2nd 2015 at 09:18 UTC. Enclosed
very nice LRPT picture of Europe was received by Enrico
IW2AGJ from Meteor-M N2 during its orbit #1656 on November
2nd 2015 at 09:18 UTC.
|
In January 2015 I also
started to receive LRPT pictures from Meteor-M N2. If
you click on the icon to the right you will get
to the respective collection of pictures. |

|
Relek
RELEC
MKA-PN2
MKA-FKI 2
#40070
(2014-037B) |
Relek,
also known as MKA-PN 2, is a Russian designed and built
smallsat will study electron precipitation via a magnetospheric
payload.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
July 8th
2014 |
253 kg |



|
DX-1
#40071
(2014-037C) |
DX-1, from Dauria
Aerospace, will track navigation on waterways throughout
North America, Northern Europe, as well as Russia. This
smallsat carries an AIS payload on a proprietary platform
that was completely designed and built by the company
and takes advantage of the ongoing growth in the remote
sensing industry.
Parameters of the
radio beacon mode are:
Carrier frequency:
438.225 MHz [it is understood there is a 145 MHz command
uplink]
The protocol used: AX.25
Call Sign source: DSC001
Call Sign Receiver: Dauria
Size
TMI frame within AX.25 packet: 55 bytes
Speed:
9600 bit / s
Modulation
GFSK
It is understood
the satellite will also be using the following frequencies:
162.0125-162.0375
MHz Uplink – AIS ship tracking RX
2269.5-2270.5
MHz Downlink – Data TX
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
July
8th 2014 |
27
kg |
 On
July 19th 2014 at 19:51 UTC
Davide IW0HLG received the signal of DX-1. Decoded telemetry
kindly provided by On
July 19th 2014 at 19:51 UTC
Davide IW0HLG received the signal of DX-1. Decoded telemetry
kindly provided by  Davide
IW0HLG. Davide
IW0HLG.
|

|
SkySat-2
#40072
(2014-037D) |
SkySat-2,
the next smallsat iteration from SkyBox Imaging, will
be primarily focused on Earth imaging and will offer
resolutions of up to 3.3 feet (one meter). This smallsat
is the second of the company's planned constellation
of 24 satellites. SkySat-2's main TT&C downlink
is 8375 MHz (RHCP), the backup downlink is 8380 MHz
(RHCP). Data downlinks in 8PSK 45MSps are at 8075 MHz,
8200 MHz and 8325 MHz. Uplinks are at 2081 MHz (RHCP)
and 2083 MHz (RHCP).
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
July 8th
2014 |
90 kg |

|
AISSat-2
#40075
(2014-037G) |
AISSat-2, which
is funded by the Norwegian Space Center with additional
support from the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment,
is dedicated to AIS observations from space and is a
follow-on mission from the earlier launched AISSat-1,
which proved to be enormously successful. CMOS Image
Demonstrator from Open University is packing a new form
of image sensor that will be tested for viability in
the face of space radiation, as well as engaging in
the capture of images of Earth. |
July
8th 2014 |
6,5
kg |
 Mike
DK3WN received the CW signal of AISSAT-2 on June 30th
2014 at 09:51 UTC. Recording kindly provided by Mike
DK3WN. Mike
DK3WN received the CW signal of AISSAT-2 on June 30th
2014 at 09:51 UTC. Recording kindly provided by Mike
DK3WN.
|


|
TechDemoSat-1
TDS-1
#40076
(2014-037H) |
TechDemoSat-1
(TDS-1), from Surrey Satellite Technology Limited (SSTL),
is, basically, an on orbit test facility for a variety
of payloads and software applications developed in the
United Kingdom. There are eight payloads aboard TDS-1,
which include a new form of battery charge regulator;
new cell designs on two of the smallsat's solar panels;
a computer system that will enable the remote control
of various software experiments; and a self-destruction
technology that uses a sail to force the craft out of
orbit to burn up in the Earth's atmosphere.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
July 8th
2014 |
150 kg |


|
Meridian
7
Meridian 17 L
#40296
(2014-069A) |
Meridian 7 is a Russian
military/government communications satellite launched
on a Soyuz 2-1a rocket with a Fregat upper stage from
Plesetsk, Russia. Meridian combines the military and
civilian tasks of the former Molniya-1 and Molniya-3
satellites, together with the clandestine communications
function of the outgoing LEO Parus satellites. Meridian
7 has a highly elliptical orbit (HEO) with an inclination
of 63°, also called Molniya orbit. Meridian 7 has
multiple transponders:
P-Band downlink: approx.
278 MHz 1 MHz wide (unconfirmed),
UHF-Band downlink:
484.250 MHz 38 kHz wide,
C-Band downlink: approx.
3600 MHz. |
Oct.
30th 2014 |
>
2000 kg |
  Paul Marsh
received on the C-Band downlink at 3610 MHz a low data
rate FSK signal of Meridian 7 on January 2nd
2015 at 16:20 UTC. Audio recording and spectrum plot
kindly provided by Paul Marsh M0EYT. Paul Marsh
received on the C-Band downlink at 3610 MHz a low data
rate FSK signal of Meridian 7 on January 2nd
2015 at 16:20 UTC. Audio recording and spectrum plot
kindly provided by Paul Marsh M0EYT.
|

|
Hodoyoshi-1
#40299
(2014-070B) |
On Thursday, November
6th at 07:35:49 UTC a Dnepr rocket carrying the primary
payload Asnaro-1 and four microsatellites was launched
from Dombarovsky near Yasny. Kosmotras report all spacecraft
have been inserted into their target orbits.
Hodoyoshi-1
is an experimental Earth-observation satellite built
by the University of Tokyo. The 60kg satellite features
a camera with a ground resolution of 6.7m. It transmits
on 467.674 MHz.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Nov 6th
2014 |
60 kg |

|
ChubuSat-1
Kinshachi-1
#40300
(2014-070C) |
ChubuSat-1 (Kinshachi-1)
is a 50kg micro-satellite built by Nagoya University
and Daido University to conduct space debris observations.
It tranmits on 437.485 MHz CW and AX.25. The corresponding
Digipeater uplink frequency is 145.980 MHz. Signal reports
have been received from ChubuSat-1. |
Nov
6th 2014 |
50
kg |
 Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW signal of ChubuSat-1 on May 9th
2015 at 11:19 UTC. Recording kindly provided
by Francisco EA7ADI. Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW signal of ChubuSat-1 on May 9th
2015 at 11:19 UTC. Recording kindly provided
by Francisco EA7ADI.
|

|
QSat-EOS
Tsukushi
#40301
(2014-070D) |
QSat-EOS
(Kyushu Satellite for Earth Observation System Demonstration)
or Tsukushi is a 50kg micro-satellite built by Kyushu
University (the ancient name of Kyushu is Tsukushi).
The Earth-observation satellite is cube shaped with
a sidelength of approx. 50cm. Its average power consumption
is 74 Watts provided by GaAs solar cells. RF communication
up- and downlinks are in S-band and Ku-band:
- Data
downlink: Ku-band 33 Mbit/s (5.0 Watts)
- Data uplink:
Ku-band 10 Mbit/s
- TT&C downlink: S-band 1
or 100 kbit/s (1.0 Watt)
- TT&C uplink: S-band
1 kbit/s
The S-band signals use AX.25 protocol,
the uplink is FSK modulated, the downlink is GMSK modulated.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Nov 6th
2014 |
50 kg |
 |
Tsubame
#40302
(2014-070E) |
Tsubame
(English Swallow) is a 50kg micro-satellite built by
Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo University of Science
and JAXA. Its primary purpose is to demonstrate attitude
control and to measure polarized gamma-ray bursts. It
features a small high resolution optical camera. Its
downlinks are at 437.275 MHz CW (0.1 Watts) and 437.505
1200bd AFSK AX.25 SRLL (0.5 Watts). The primary downlink
is in S-Band (BPSK, CCSDS). Uplinks are at 140 MHz (1200bd
AFSK AX.25 and DTMF) and S-Band (PCM-PSK-PM). Signal
reports have been received from Tsubame from DK3WN. |
Nov
6th 2014 |
50
kg |
  Davide
IW0HLG received the CW signal of Tsubame on December
13th 2014 at 10:10 UTC on 437.275
MHz. Recording and waterfall plot kindly provided by
Davide IW0HLG. Davide
IW0HLG received the CW signal of Tsubame on December
13th 2014 at 10:10 UTC on 437.275
MHz. Recording and waterfall plot kindly provided by
Davide IW0HLG.
|
 On January
5th 2015 at 12:28 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW signal of TSUBAME. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On January
5th 2015 at 12:28 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the CW signal of TSUBAME. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|

|
SpinSat
#40314
(1998-067FL) |
SpinSat is a 56cm
diameter spherical satellite was developed by Naval
Research Laboratory (NRL). Its primary purpose is to
calibrate the space surveillance network. As it features
inly primary batteries and no solar cells its lifetime
will be limited to 3 to 6 months. SpinSat was brought
to the ISS on September 21st 2014.
On November 28th 2014
after 17:00 UTC it was released from ISS using the airlock
of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). It uses 4 antennas
equally space around the equator of the sphere.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Nov
28th 2014 |
57 kg |

|
FIREBIRD
3
FIREBIRD FU3
FIREBIDR II-A
#40377
(2015-003B) |
FIREBIRD (Focused
Investigations of Relativistic Electron Burst Intensity,
Range, and Dynamics) is a CubeSat dual satellite mission
examining the spatial scale and spatial temporal ambiguity
of magnetospheric microbursts. FIREBIRD 3 features a
19200 bd FSK downlink on 437.395 MHz and 437.405 MHz. |
Jan
31st 2015 |
2
kg |
 On March
10th 2015 at 18:02 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the downlink signal of FIREBIRD 3. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On March
10th 2015 at 18:02 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the downlink signal of FIREBIRD 3. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 Also
on May 7th 2015 at 18:11 UTC
Francisco EA7ADI received the downlink signal of FIREBIRD
3. Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. Also
on May 7th 2015 at 18:11 UTC
Francisco EA7ADI received the downlink signal of FIREBIRD
3. Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
  Mineo Wakita JE9PEL received and decoded the 19200bd
FSK downlink signal of Firebird-3 on October 17th
2017 at 10:26 UTC on 437.391 MHz. Recording and screenshot
kindly provided by Wakita-san JE9PEL.
Mineo Wakita JE9PEL received and decoded the 19200bd
FSK downlink signal of Firebird-3 on October 17th
2017 at 10:26 UTC on 437.391 MHz. Recording and screenshot
kindly provided by Wakita-san JE9PEL.
|

|
FIREBIRD
4
FIREBIRD FU4
FIREBIRD II-B
#40378
(2015-003C) |
FIREBIRD (Focused
Investigations of Relativistic Electron Burst Intensity,
Range, and Dynamics) is a CubeSat dual satellite mission
examining the spatial scale and spatial temporal ambiguity
of magnetospheric microbursts. FIREBIRD 4 features a
19200 bd FSK downlink on 437.219 MHz and 437.230 MHz. |
Jan
31st 2015 |
2
kg |
 On April
30th 2015 at 18:46 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the downlink signal of FIREBIRD 4. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. On April
30th 2015 at 18:46 UTC Francisco
EA7ADI received the downlink signal of FIREBIRD 4. Recording
kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
  Mineo
Wakita JE9PEL received and decoded the 19200bd FSK downlink
signal of Firebird-4 on October 17th
2017 at 10:27 UTC on 437.214 MHz. Recording and screenshot
kindly provided by Wakita-san JE9PEL. Mineo
Wakita JE9PEL received and decoded the 19200bd FSK downlink
signal of Firebird-4 on October 17th
2017 at 10:27 UTC on 437.214 MHz. Recording and screenshot
kindly provided by Wakita-san JE9PEL.
|


|
GRIFEX
#40379
(2015-003D) |
GRIFEX
(GEO-CAPE ROIC In-Flight Performance Experiment) is
a 3U CubeSat built my JPL/CalTech/University of Michigan.
it is a technology validation mission, sponsored
by NASA's Earth Science Technology Office, and launched
on a Delta-7320-10C rocket from Vandenberg AFB, California,
in a LEO orbit.
It will advance the technology required
for the future space-borne measurements of atmospheric
composition from GEO, relevant to climate change, as
well as future missions that require advanced detectors
in support of the Earth Science Decadal Survey.
It performs engineering assessment of a JPL-developed
all digital in-pixel high frame rate Read-Out Integrated
Circuit (ROIC). Its high throughput capacity will enable
the proposed GEO-CAPE (Geostationary Coastal and Air
Pollution Events) mission concept to make hourly high
spatial and spectral resolution measurements of rapidly
changing atmospheric chemistry and pollution with the
Panchromatic Fourier Transform Spectrometer (PanFTS)
instrument.
GRIFEX's downlink frequency is 437.482
kHz using GMSK modulation and AX.25 9600bps encoding.
The output power is <1 Watt and the beacon transmits
in a 10 sec period with the callsign CQ>KD8SPS. |
Jan
31st 2015 |
4
kg |
 On April
2nd 2015 at 18:08 UTC Darko
9A3LI received the 9600bps signal of GRIFEX
on 437.482 MHz. Recording kindly provided by Darko
9A3LI. On April
2nd 2015 at 18:08 UTC Darko
9A3LI received the 9600bps signal of GRIFEX
on 437.482 MHz. Recording kindly provided by Darko
9A3LI.
|

|
Fajr
#40387
(2015-006A) |
The
Iranian satellite Fajr (i.e. 'Dawn') was launched on
2015-02-02 just before 09:00 UTC from Semnan launch
center with a Safir rocket. The 50 kg satellite (40387,
2015-006A), Iran's fourth satellite, has a cold gas
thruster, so it can change its orbit. It carries a camera
for earth observations. It should have a telemetry downlink
on 437.538 MHz and a command uplink in the 2 m band.
No signal reports have been seen.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Feb 2nd
2015 |
50 kg |

|
MICROMAS
MicroMAS-1
#40457
(1998-067GA) |
MicroMas
(Micro-sized Microwave Atmospheric Satellite-1) is a
3U Cubesat released on March 4th
2015 from ISS together with LambdaSat, GearrSat and
TechEdSat4. MicroMAS
is a nanosatellite (3U CubeSat) technology demonstration
mission, a joint project of MIT/LL (Massachusetts Institute
of Technology/Lincoln Laboratory), MIT/SSL (Space Systems
Laboratory) and the University of Massachusetts
at Amherst. -The nanosatellite is hosting a passive
microwave spectrometer with nine channels operating
near the 118.75 GHz oxygen absorption line. The
spacecraft transceiver is a half-duplex L-3 Communications
Cadet UHF Nanosatellite radio. The uplink frequency
is 450 MHz at ~9.6 kbit/s GFSK (19.2 kbit/s with FEC),
and the downlink frequency is 468 MHz at ~1.5 Mbit/s
OQPSK (3 Mbit/s with FEC). The average data rate from
the payload to the bus for downlink is ~19.2 kbit/s.
The radio includes a ~4 GB memory buffer which stores
payload data and housekeeping telemetry between ground
station passes.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Mar 4th
2015 |
4.25
kg |


|
LambdaSat
KK6DFZ
#40458
(1998-067GB) |
LambdaSat
is a Cubesat released on March 4th
2015 from ISS together with MicroMas, GearrSat and TechEdSat4.
The naming of the Lambda-sat satellite came from the
Greek letter L, lambda, a
reminder of Hellas, Helios, the Greek
word Thalassa for sea, the Greek word
Lithos which directly translates to stone
(meaning “Land of Light”). Initiated by Prof. Periklis
Papadopoulos, it was built by Greek volunteers in Silicon
Valley, California, USA. It includes a AIS receiver,
an Iridium modem, a graphene experiment as well as an
UHF receiver and transmitter. The UHF-transmitter of
LambdaSat transmits 1200bps AFSK AX.25 data packets
on its downlink is 437.462 MHz using 1W output power.
The callsign is KK6DFZ.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Mar 4th
2015 |
1
kg |



|
DeOrbitSail
#40719
(2015-032E) |
The DeorbitSail
is a 3U (10 cm by 10 cm by 34 cm) CubeSat satellite
which was launched on a PSLV-XL rocket from Sriharikota
in India.
It will deploy a
4m by 4m sail that will demonstrate rapid deorbiting.
The deorbiting capability of the DeorbitSail satellite
is due to increased aerodynamic drag from the large
surface area of the deployed sail in a Low Earth Orbit
(LEO) and solar radiation pressure.
The DeorbitSail
project is a cooperation between Surrey Space Centre
(UK), Caltech (USA), DLR (Germany), EADS Astrium (France),
Stellenbosch University (South Africa), University of
Patras (Greece), Athena-SPU (Greece), Middle-Eastern
Technical University (Turkey), Surrey Satellite Technology
Limited (SSTL) (UK), ISIS (Netherlands).
DeorbitSail features
power, communications, attitude control and data handling
components in addition to its densely packed sail and
deployment system. It features a 1200 bpsk BPSK telemetry
downlink on 145.975 MHz. |
July
10th 2015 |
3
kg |
 DeOrbitsail
was received and recorded on July 18th
2015 at 08:00 UTC on 145.975 MHz in USB by DD1US. DeOrbitsail
was received and recorded on July 18th
2015 at 08:00 UTC on 145.975 MHz in USB by DD1US.
|
  On July 26th 2015 at 17:12
UTC Francisco EA7ADI also received and decoded the 1200
bpsk BPSK downlink signal of DeOrbitSail on 145.975
MHz. Recording and screen shot of the decoder kindly
provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
On July 26th 2015 at 17:12
UTC Francisco EA7ADI also received and decoded the 1200
bpsk BPSK downlink signal of DeOrbitSail on 145.975
MHz. Recording and screen shot of the decoder kindly
provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|


|
Meteosat
11
MSG 4
#40732
(2015-034A) |
Meteosat-11 is the 4th
and last flight unit of the Meteosat Second Generation
(MSG) programme. Once MSG 4 became fully operational
it was renamed to Meteosat-11. In February 2018 it replaced
Meteosat 10 at the geostationary orbit above Europe
at 0° longitude. It ensures data continuity for
weather forecasting and plays a crucial role in ‘nowcasting’
high-impact weather events and climate research. The
MSG-4 satellite has a height of 3.7 m and a diameter
of 3.2 m. Its launch mass is 2000 kg and designed lifespan
is seven years.
All four MSG satellites
are operated by Eumetsat – the European Organisation
for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites –
with ESA responsible for their design, development and
in-orbit delivery.
Meteosat 11 transmits LRIT data (128 kbps) at
1691 MHz and HRIT data (1.0 Mbps) at 1695.150 MHz. In
addition there is a downlink to the primary ground station
(3.27 Mbps) at 1686.83 MHz. Finally it includes a (100
kbps) downlink at 1675.281 MHz retransmitting the DCP
reports which it receives around 402 MHz. |
July
15th 2015 |
2040
kg |
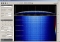  DD1US
received the LRIT downlink signal on 1691 MHz on February
21st 2018 at 16:30 UTC. The soundfile was generated
by demodulating DD1US
received the LRIT downlink signal on 1691 MHz on February
21st 2018 at 16:30 UTC. The soundfile was generated
by demodulating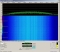 the signal in CW mode.
the signal in CW mode.
|

|
SERPENS
#40897
(1998-067GX) |
On
September 17th 2015
the Brazilian SERPENS 3U CubeSat carrying an amateur
radio payload, call sign PY0ESA, was deployed from the
International Space Station (ISS).
It features
the following modi:
- 145.980 MHz 9600bd AX.25 beacon
using GFSK modulation transmitted every 10 seconds
- 437.365 MHz beacon using CW and 1200bd MSK modulation
(CSP protocol)
- 437.525 MHz store-and-foreward
system using 1200bd GMSK modulation collecting from
environmental sensors on Earth and transmitting them
to University ground stations. |
Sept
17th 2015 |
4
kg |
  On September 24th 2015 at 19:41
UTC Tetsu-san JA0CAW received and recorded Serpens on
437.365 MHz. Recording and waterfall plot kindly provided
by Tetsu-san JA0CAW.
On September 24th 2015 at 19:41
UTC Tetsu-san JA0CAW received and recorded Serpens on
437.365 MHz. Recording and waterfall plot kindly provided
by Tetsu-san JA0CAW.
|
 Francisco
EA7ADI received the 1200bd GMSK downlink of Serpens
on 437.365 MHz on October 5th2015
at 19:10 UTC. Recording kindly provided by Francisco
EA7ADI. Francisco
EA7ADI received the 1200bd GMSK downlink of Serpens
on 437.365 MHz on October 5th2015
at 19:10 UTC. Recording kindly provided by Francisco
EA7ADI.
|

|
LQSat
#40958
(2015-057A) |
On
October 7th 2015
the Chinese microsatellite LQSat for technology demonstration
designed by CIOMP (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine
Mechanics and Physics) was launched as part of the Jilin-1
mission. Its main payload is a camera with 2m resolution.
Satellite dimensions are 0.4m x 0.4m x 0.6m. The UHF
downlink at 437.650 MHz and 27dBm features a 4k8 bps
MSK CSP packet data and 25 wpm CW beacon. Ths SHF doenlink
at 2404.000 MHz and 30 dBm features a 1 Mbps QPSK transmitter.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Oct 7th
2015 |
54 kg |

|
BisonSat
#40968
(2015-058E) |
BisonSat or Nwist
Q??iq??áy is an educational 1U CubeSat
designed and built by students of the Salish Kootenai
College (SKC), Montana.The primary purpose of the mission
is educational, but also has a science objective
of using broad-band visible light orbital imagery
to study atmospheric aerosols, cloud formation,
and various hydrologic processes. It is solar powered
and carries a SKC-designed camera and a radio
for receiving commands and transmitting data. BisonSat
is passively attitude stabilized by a bar magnet inside,
which will line up with Earth's magnetic field. This
allows for earth imaging, where the magnetic field has
a large downward vertical component. which is especially
the case over Montana. Over much of North America
the camera will be pointed to within 10º-30º
of nadir.
At perigee, the 35 mm optic yields a 8.4º field
of view,
and a 69 km maximum ground swath width. Best resolution
is 43 m ground sampling distance at nadir. The
UHF downlink at 437.375 MHz transmits a 9k6 bps GMSK
AX.25 packet radio signal every 60 sec. |
Oct
8th 2015 |
1
kg |
 Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9k6 FSK downlink of BisonSat on
437.414 MHz on February 10th2016
at 19:12 UTC. He used a IC7000 receiver in USB mode.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9k6 FSK downlink of BisonSat on
437.414 MHz on February 10th2016
at 19:12 UTC. He used a IC7000 receiver in USB mode.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|
 Jan PE0SAT
received the 9600bd FSK downlink signal of BisonSat
On February 15th 2016 at 17:45
UTC on 437.414 MHz. Enclosed I/Q recording kindly provided
by Jan van Gils PE0SAT. Jan PE0SAT
received the 9600bd FSK downlink signal of BisonSat
On February 15th 2016 at 17:45
UTC on 437.414 MHz. Enclosed I/Q recording kindly provided
by Jan van Gils PE0SAT.
|



|
Elektro-L2
Electro-L N2
#41105
(2015-074A) |
Elektro-L2 is a
Russian Weather satellite built by Roskosmos. It was
launched on a Zenit-3SLBF rocket from Baikonur into
a geostationary orbit on 78 degree East. Later it was
transferred to 14.5 degree West. Its main purpose is
to provide weather pictures from Asia, Middle East and
the Indian Ocean featuring 3 visual and 7 infrared cameras.
The resolution of the visual cameras are 1km/pixel and
4km/pixed of the infrared cameras. The sensor data is
transmitted to Earth in X-band with data rates between
2.56 and 15.36 Mbit/s. Electro-L2 also supports the
COSPAS-SARSAT-system with a downlink at 1.54 GHz (4
Watts). Finally Elektro collects data from ground stations
on 400 MHz and LEOs on 470 MHz and transmits them back
to Earth on 1.7 GHz. Whether also a LRIT downlink signal
at 1691 MHz might be activated as already active on
Elektro-L3 remains to be seen. |
Dec.
11th 2015 |
1700
kg |
 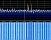 Enclosed
signal was recorded on 1697.043 Mhz in USB on January
7th 2018 at 18:32 UTC by DD1US.
The spectrum was recorded on the same day at 16:12 UTC. Enclosed
signal was recorded on 1697.043 Mhz in USB on January
7th 2018 at 18:32 UTC by DD1US.
The spectrum was recorded on the same day at 16:12 UTC.
|

|
Athenoxat-1
#41168
(2015-077C) |
Athenoxat
1 (Athene Noctua Experimental Satellite) is a 3U Cubesat
developed by Microspace Rapid Pte Ltd. of Singapore.
Its main purpose is to demonstrate the functionality
of a night vision optical payload on a Cubesat Class
Nanosatellite. It was launched on an Indian PSLV-CA
rocket
into a near equatorial orbit with an altitude of 550
km and an inclination of 15°. Thus it is not visible
in Central Europe. It
features a 2400bps FM MSK UHF and a higher speed S-Band
downlink. It also features a CW telemetry
beacon transmitting on 437.485 MHz and uses the callsign
ATX1. |
Dec.
16th 2015 |
3
kg |
 On December
16th 2015 at 23:52 UTC Roland
PY4ZBZ received the CW beacon of Athenoxat-1 on 437.490
MHz. Recoding kindly provided by Roland PY4ZBZ. On December
16th 2015 at 23:52 UTC Roland
PY4ZBZ received the CW beacon of Athenoxat-1 on 437.490
MHz. Recoding kindly provided by Roland PY4ZBZ.
|
 On
December 18th 2015 Athenoxat-1
took a picture of the Earth with its fisheye camera. On
December 18th 2015 Athenoxat-1
took a picture of the Earth with its fisheye camera.
|




|
AggieSat4
AGS4
#41313
(1998-067HP) |
AggieSat-4 was ejected
from the International Space Station on January 29th
2016 using the SSIKLOPS (Space Station Integrated Kinetic
Launcher for Orbital Payload Systems) deployment mechanism.
It is part of the second LONESTAR (Low Earth Orbiting
Navigation Experiment for Spacecraft Testing Autonomous
Rendezvous and Docking) mission. The other satellite
is BEVO-2 which will be released by Aggiesat-4 later.
AggieSat4 was developed and built by Texas A&M University
and measures 75x75x35cm. It is three-axis-stabilized.
AggieSat4 features two low-data-rate (LDR) radios, a
high-data-rate (HDR) radio, a crosslink radio for short
range communication with the BEVO-2 satellite and a
DRAGON GPS payload. Its main objectives are: demonstration
of 3-axis-stabilization, collection of GPS data, recording
video of the deployment of the BEVO-2 satellite using
its 2MP camera, rendezvous investigations with BEVO-2.
AggieSat-4 features a telemetry beacon
downlink on 436.250 MHz in 9k6bd FSK or 153k6 FSK. The
beacon transmits once every 60 sec using the callsign
WH2XGN. |
Jan.
29th 2016 |
55
kg |
 Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9k6 FSK downlink of Aggiesat-4 on
436.250 MHz on February 2nd2016
at 18:07 UTC. He used a IC7000 receiver in USB mode.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI. Francisco
EA7ADI received the 9k6 FSK downlink of Aggiesat-4 on
436.250 MHz on February 2nd2016
at 18:07 UTC. He used a IC7000 receiver in USB mode.
Recording kindly provided by Francisco EA7ADI.
|




|
BEVO-2
#413xx
(1998-067Hxx) |
BEVO-2 was
built by students at the University of Texas. I was
released inside of AggieSat-4 from the International
Station on January 29th 2016
and was planned to be released by Aggiesat-4 using an
ISPOD deployment system at a later point in time. BEVO-2
uses the 3U Cubesat form factor and measures 10x10x34cm.
BEVO-2 features a UHF/VHF terminal for data downlink
to and command uplink from ground. In addition it features
qa crosslink radio unit for communication with AggieSat-4.
With its cold gas thrusters it will perfrom maneuver
exercises with AggieSat-4.
BEVO-2 features a telemetry beacon
downlink on 437.325 MHz in 38k4 FSK and CW.
BEVO-2 was prematurely deployed from
AggieSat-4 and never activated. |
Jan. 29th
2016 |
4.2 kg |



|
KMS-4
Kwangmyongsong
4
#41332
(2016-009A) |
Kwangmyongsong
4 is a North Korean earth observation satellite built
by the National Aerospace Development Administration
(NADA). Reportedly
the satellite carries some earth observation equipment.
Initial unconfirmed images of KMS-4 show a cubic body
with two deployable solar arrays and two camera apertures
on the nadir side.
Kwangmyongsong 4
launched on February 7th 2016
on an Unha-3 rocket from the Sohae Satellite Center
in Ch’olsan County, North P’yongan Province. It entered
a sun-synchronous orbit of 465 km × 501 km with
an inclination of 97.5°. No signals have been detected
from the satellites and ground observations showed,
that it was initially tumbling. An analysis by Bob Christy
suggests a significant shortfall in 3rd stage
performance of the Unha-3 launch vehicle.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Feb. 7th
2016 |
200 kg |

|
Mozi
QUESS
QSS
#41731
(2016-051A) |
Mozi
(the name of a Chinese scientist who lived about 2500
years ago) is the first spacecraft to establish quantum
communications between space and Earth by creating entangled
photon pairs over great distances and testing the principles
of quantum teleportation. It is also named QUESS (Quantum
Experiments at Space Scale) or QSS (Quantum Science
Satellite). It was
developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and launched
on August 15th 2016
from Jiquan, PRC, on a Long March 2D rocket.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Aug. 15th
2016 |
500 kg |

|
LX-1
Lixing
1
#41733
(2016-051C) |
Lixing
1 was a Chinese satellite with the mission to research
the rarified upper atmosphere. It was developed
by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and launched
on August 15th 2016
from Jiquan, PRC, on a Long March 2D rocket. After
its launch together with QSS it lowered its orbit to
124 km × 140 km, 97.4°, the lowest orbit of
an active spacecraft ever. LX-1 reentered after
only 5 days on August 19th 2016.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Aug. 15th
2016 |
110 kg |


|
Himawari-9
#41836
(2016-064A) |
The satellite
Himawari-9 (sunflower) was launched on H-II/AF31 into
a geostationary orbit at 140°W. It is a meteorology
satellite operated by Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA).
Its downlinks are:
CDAS 18284.6
MHz lin.
pol. at 66Mbps
DCS 18399-18400
MHz lin. pol. at 0.1/0.3/0.6 kbps
DCS
402-402.4 MHz RHCP
at 0.1/0.3/0.6 kbps
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Nov. 2nd
2016 |
3500 kg |

|
TY-1
#41844
(2016-066D) |
Mission:
technical experiment,
TT&C: 437.500 MHz, bandwidth
300 kHz |
Nov 9th
2016 |
|
|
KS-1Q
#41845
(2016-066E) |
Built by
Kechuang Aerospace Forum. The mission is a technical
experiment. KS-1Q was intentionally not separated from
the final stage of rocket CZ-11(Y2).
The
final stage was originally expected to be in orbit for
up to 30 days before re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere
but reports indicate the orbit is 504 x 1030 km which
could give an orbital lifetime of years.
TT&C: 436.500 MHz, 20 kbps GMSK, every 8-10 sec |
Nov
9th 2016 |
|
  Wakita-san
JE9PEL received a burst of the 20 kbps GMSK downlink
signal of KS-1Q on November 20th
2016 from 08:01 to 08:17 UTC on 436.491 MHz. He reports
to have received the 20kbps GMSK signal every 4'40".
Audio recording and waterfall display screen shot kindly
provided by Wakita-san JE9PEL. Wakita-san
JE9PEL received a burst of the 20 kbps GMSK downlink
signal of KS-1Q on November 20th
2016 from 08:01 to 08:17 UTC on 436.491 MHz. He reports
to have received the 20kbps GMSK signal every 4'40".
Audio recording and waterfall display screen shot kindly
provided by Wakita-san JE9PEL.
|

|
Pegasus-1
#41846
(2016-066F) |
Mission:
technical experiment,
TT&C: 468.000MHz |
Nov 9th
2016 |
|
Picture |
Object
name
#NORAD |
Description |
Launch
Date |
Weight |