Picture |
Object
name
#NORAD |
Description |
Launch
Date |
Weight |

|
HEOS 2
HEOS-A2
#05814
(1972-005A) |
  HEOS
2 was built by ESRO (the European Space Research Organisation).
This spin stabilized satellite traveled in extremely
elongated orbits in order to study the interplanetary
magnetic field and solar and cosmic ray particles outside
the Earth’s magneto-sphere. It studied especially high
latitude magneto-sphere and the region around the northern
neutral point. It transmitted telemetry on 136.68 MHz
(5.9 W). Control uplink frequency was 148.250 MHz. Both
recordings made on August 15th
1973 in AM mode on 136.680 MHz by Greg Roberts. HEOS
2 was built by ESRO (the European Space Research Organisation).
This spin stabilized satellite traveled in extremely
elongated orbits in order to study the interplanetary
magnetic field and solar and cosmic ray particles outside
the Earth’s magneto-sphere. It studied especially high
latitude magneto-sphere and the region around the northern
neutral point. It transmitted telemetry on 136.68 MHz
(5.9 W). Control uplink frequency was 148.250 MHz. Both
recordings made on August 15th
1973 in AM mode on 136.680 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Jan 31st
1972 |
123 kg |

|
TD 1A
#05879
(1972-014A) |
 TD-1A
(Thor Delta 1) Astronomical Celestial Observation Satellite.
It carried seven experiments devoted to astrophysical
studies. Recorded on 137.740 MHz using an SSB receiver
on October 30th 1974 by Greg
Roberts. TD-1A
(Thor Delta 1) Astronomical Celestial Observation Satellite.
It carried seven experiments devoted to astrophysical
studies. Recorded on 137.740 MHz using an SSB receiver
on October 30th 1974 by Greg
Roberts.
|
Mar 12th
1972 |
472 kg |
 TD-1A
received on 136.050 MHz on May 17th
1972 by Greg Roberts. TD-1A
received on 136.050 MHz on May 17th
1972 by Greg Roberts.
|
 TD-1A
received on October 24th 1973
on 136.050 MHz in AM by Greg Roberts. TD-1A
received on October 24th 1973
on 136.050 MHz in AM by Greg Roberts.
|

|
LANDSAT
1
(ERTS-1)
#06126
(1972-058A) |
 Earth
Resources Technology Satellite. Its objective was to
obtain coverage of the United States and other major
land masses with multi-spectral, high spatial resolution
(60 m) images of solar radiation reflected from the
earth's surface. The tracking beacon transmitted on
137.860 MHz at 2 W. Telemetry on command was transmitted
in S-Band on 2229.5 MHz (20 W), 2265.5 MHz (20 W), 2287.5
MHz (1 W). Recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in AM by Greg Roberts. Earth
Resources Technology Satellite. Its objective was to
obtain coverage of the United States and other major
land masses with multi-spectral, high spatial resolution
(60 m) images of solar radiation reflected from the
earth's surface. The tracking beacon transmitted on
137.860 MHz at 2 W. Telemetry on command was transmitted
in S-Band on 2229.5 MHz (20 W), 2265.5 MHz (20 W), 2287.5
MHz (1 W). Recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in AM by Greg Roberts.
|
Jul 23rd
1972 |
950 kg |
 Recorded
on Dec 14th 1973 in FM by Greg
Roberts. Recorded
on Dec 14th 1973 in FM by Greg
Roberts.
|

|
METEC
MTS
(Explorer 46)
#06142
(1972-061A) |
 METEC
(Meteoroid Technology Satellite) measured the meteoroid
penetration rates in a bumper-protected target as well
as meteoroid velocity and flux distribution. Recorded
on 136.320 MHz using an SSB receiver by Greg Roberts. METEC
(Meteoroid Technology Satellite) measured the meteoroid
penetration rates in a bumper-protected target as well
as meteoroid velocity and flux distribution. Recorded
on 136.320 MHz using an SSB receiver by Greg Roberts.
|
Aug 13th
1972 |
90 kg |
 Recorded
on June 7th 1975 on 136.320
MHz by Greg Roberts. Recorded
on June 7th 1975 on 136.320
MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
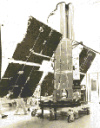
  Explorer
46 recorded twice on October 24th
1973 on 136.320 MHz in AM mode by Greg Roberts. Explorer
46 recorded twice on October 24th
1973 on 136.320 MHz in AM mode by Greg Roberts.
|
  Recorded
twice on August 30th 1974 by
Greg Roberts. Recorded
twice on August 30th 1974 by
Greg Roberts.
|
|
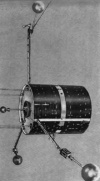
OAO-3
Copernicus
#06153
(1972-065A) |
 Orbiting
Astronomical Observatory (OAO-3, OAO-C) was also known
as Copernicus. Frequencies used were 136.260 MHz and
136.440 MHz. Recorded on December 14th
1973 using different demodulators by Greg Roberts. Orbiting
Astronomical Observatory (OAO-3, OAO-C) was also known
as Copernicus. Frequencies used were 136.260 MHz and
136.440 MHz. Recorded on December 14th
1973 using different demodulators by Greg Roberts.
|
Aug
21st 1972 |
2150
kg |
 OAO-C
Copernicus recorded on Oct 24th
1973 in AM probably on 136.440 MHz by Greg Roberts. OAO-C
Copernicus recorded on Oct 24th
1973 in AM probably on 136.440 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
 Recorded
in AM mode on Sept 1st 1975
by Greg Roberts. Recorded
in AM mode on Sept 1st 1975
by Greg Roberts.
|

|
NOAA 2
(ITOS-D)
#06235
(1972-082A) |
 Meteorological
satellite providing day and night cloud cover data.
NOAA-2 relied entirely on scanning radiometers for imagery.
Tracking and telemetry was transmitted with 250 mW on
136.770 MHz. Telemetry on demand was on 137.500 MHz,
137.620 MHz or 1697.500 MHz (5 W). APT transmission
recorded on Dec 14th 1973 in
FM by Greg Roberts. Meteorological
satellite providing day and night cloud cover data.
NOAA-2 relied entirely on scanning radiometers for imagery.
Tracking and telemetry was transmitted with 250 mW on
136.770 MHz. Telemetry on demand was on 137.500 MHz,
137.620 MHz or 1697.500 MHz (5 W). APT transmission
recorded on Dec 14th 1973 in
FM by Greg Roberts.
 The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark B. The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark B.
|
Oct 15th
1972 |
409 kg |
 The beacons
on the NOAA satellites are relatively powerful and can
be heard without much difficulty using the FM mode of
receivers. This was shown here on December 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. The beacons
on the NOAA satellites are relatively powerful and can
be heard without much difficulty using the FM mode of
receivers. This was shown here on December 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
 NOAA
2 ( aka ITOS-D) recorded either on 137.500 MHz or 137.620
MHz in AM mode on August 15th
1973 by Greg Roberts. NOAA
2 ( aka ITOS-D) recorded either on 137.500 MHz or 137.620
MHz in AM mode on August 15th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
 NOAA
2 telemetry beacon recorded either on 136.770 MHz in
AM mode on October 24th 1973
by Greg Roberts. NOAA
2 telemetry beacon recorded either on 136.770 MHz in
AM mode on October 24th 1973
by Greg Roberts.
|
|
ESRO-4
#06285
(1972-092A) |
 ESRO
4 was cylindrical in shape and was spin stabilized.
It transmitted a PCM/PM telemetry mode in three forms:
real-time telemetry at 64 bps, tape-recorder playback
and high-speed telemetry at 10240 bps. It studied the
ionosphere, auroras and solar particles. Recorded on
October 24th 1973 in AM on
137.200 MHz by Greg Roberts. ESRO
4 was cylindrical in shape and was spin stabilized.
It transmitted a PCM/PM telemetry mode in three forms:
real-time telemetry at 64 bps, tape-recorder playback
and high-speed telemetry at 10240 bps. It studied the
ionosphere, auroras and solar particles. Recorded on
October 24th 1973 in AM on
137.200 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Nov 22nd
1972 |
115 kg |



|
Aeros
1
Aeros A
#06315
(1972-100A) |
Aeros 1
was a German scientific satellite. The AEROS satellite
had a circular cylindrical shape, 0.914 m in diameter
and 0.710 m in height. It was launched into an elliptical,
polar, nearly sun-synchronous earth orbit. The spacecraft
was spin stabilized at 10 rpm and oriented with the
spin axis toward the sun. The purpose of the mission
was to study the state and behavior of the upper atmosphere
and ionospheric F region, especially with regard to
the influence of solar ultraviolet radiation. Five experiments
provided data on the temperature and density of electrons,
ions, and neutral particles, the composition of ions
and neutral particles, and solar ultraviolet flux.
Aeros 1 transmitted telemetry in
PCM/PM mode on 137.26 MHz. The transmit power was 0.15
W when transmitting 512bps and 1.5 W when transmitting
12.8 kbps. The uplink (command) frequency was 148.250
MHz.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to
 |
Dec 16th
1972 |
125.7 kg |

|
Meteor
1-14
#06392
(1973-015A) |
 Meteor
1-14 was the 14th fully operational
meteorological satellite in the Soviet Meteor 1 program
and the first to transmit over South Africa. Recorded
by Greg Roberts. Meteor
1-14 was the 14th fully operational
meteorological satellite in the Soviet Meteor 1 program
and the first to transmit over South Africa. Recorded
by Greg Roberts.
 The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark Boldyrev. The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark Boldyrev.
|
Mar 20th
1973 |
2000 kg |

|
NOAA
3
(ITOS-F)
#06920
(1973-086A) |
 Meteorological
satellite providing day and night cloud cover data.
Recorded on 137.400 MHz, 137.500 MHz or 137.620 MHz
using an SSB receiver by Greg Roberts. Meteorological
satellite providing day and night cloud cover data.
Recorded on 137.400 MHz, 137.500 MHz or 137.620 MHz
using an SSB receiver by Greg Roberts.
 The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark B. The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark B.
|
Nov
6th 1973 |
746
kg |
 The second
file was recorded on December 14th
1973 in FM by Greg Roberts. The second
file was recorded on December 14th
1973 in FM by Greg Roberts.
|

|
AE-C
(Explorer 51)
#06977
(1973-101A) |
 Explorer
51 was a scientific satellite studying the high atmosphere.
It transmitted on 137.230 MHz. It decayed on December
12th 1978. Recorded on June
7th 1975 in CW by Greg Roberts. Explorer
51 was a scientific satellite studying the high atmosphere.
It transmitted on 137.230 MHz. It decayed on December
12th 1978. Recorded on June
7th 1975 in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
Dec 16th
1973 |
658 kg |
 Recorded
on June 7th 1975 by Greg Roberts
(first in CW and then he switched during the reception
to AM). Recorded
on June 7th 1975 by Greg Roberts
(first in CW and then he switched during the reception
to AM).
|

|
Tansei 2
Tansei
MRT
MS-T2
#07122
(1974-008A) |
 Tansei
2 was a Japanese satellite with a short mission of only
17 days. It included a magnetic attitude control test
system, a housekeeping measurement system and a radio
telemetry system. Recorded on February 27nd
1974 in CW on 136.725 MHz by Greg Roberts. In AM nothing
could be heard. Tansei
2 was a Japanese satellite with a short mission of only
17 days. It included a magnetic attitude control test
system, a housekeeping measurement system and a radio
telemetry system. Recorded on February 27nd
1974 in CW on 136.725 MHz by Greg Roberts. In AM nothing
could be heard.
|
Feb 16th
1974 |
56 kg |

|
ATS-6
ATS-F
#07318
(1974-039A) |
 ATS-6
(Applications Technology Satellite-6, also called ATS-F)
was the world's first educational satellite as well
as the first experimental direct broadcast TV satellite
(DBS) in a geostationary orbit. The 3 axis stabilized
satellite transmitted with 2 Watts and used a 9.15m
dish antenna. Recorded on 136.230 MHz by Greg Roberts. ATS-6
(Applications Technology Satellite-6, also called ATS-F)
was the world's first educational satellite as well
as the first experimental direct broadcast TV satellite
(DBS) in a geostationary orbit. The 3 axis stabilized
satellite transmitted with 2 Watts and used a 9.15m
dish antenna. Recorded on 136.230 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
May 30th
1974 |
930 kg |
 Recorded
on 137.1017 MHz by Greg Roberts. Recorded
on 137.1017 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Hawkeye
1
Injun-F
(Explorer 52)
#07325
(1974-040A) |
  Hawkeye
1 was also called Neutral Point Explorer and carried
space physics experiments including a magnetometer,
an energetic plasma analyzer and an ELF-VLF wave instrument.
Data were transmitted in real time at frequencies of
136 MHz and 400 MHz at 100 bps (or 200 bps using convolutional
codes) plus wideband VLF data. Recorded at 136.290 MHz
using an SSB receiver. In the middle of the second recording
the receiver was switched to AM. Both files recorded
on October 30th 1974 by Greg
Roberts. Hawkeye
1 was also called Neutral Point Explorer and carried
space physics experiments including a magnetometer,
an energetic plasma analyzer and an ELF-VLF wave instrument.
Data were transmitted in real time at frequencies of
136 MHz and 400 MHz at 100 bps (or 200 bps using convolutional
codes) plus wideband VLF data. Recorded at 136.290 MHz
using an SSB receiver. In the middle of the second recording
the receiver was switched to AM. Both files recorded
on October 30th 1974 by Greg
Roberts.
|
June 3rd
1974 |
22.7 kg |
 Recorded
on September 6th 1975 on 136.290
MHz during a near perigee pass by Greg Roberts. Recorded
on September 6th 1975 on 136.290
MHz during a near perigee pass by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Aeros 2
Aeros B
#07371
(1974-055A) |
 Aeros
2 was a German scientific satellite. The purpose of
its mission was to study the state and behavior of the
upper atmosphere and ionospheric F region, especially
with regard to the influence of solar ultraviolet radiation.
It transmitted on 137.290 MHz. Recorded on June 7th
1975 in AM or FM by Greg Roberts. Aeros
2 was a German scientific satellite. The purpose of
its mission was to study the state and behavior of the
upper atmosphere and ionospheric F region, especially
with regard to the influence of solar ultraviolet radiation.
It transmitted on 137.290 MHz. Recorded on June 7th
1975 in AM or FM by Greg Roberts.
|
Jul 16th
1974 |
125.7 kg |
 It was
launched into an elliptical, polar, nearly sun-synchronous
earth orbit and decayed on September 25th
1975. Recorded on September 7th
1975 on 137.290 MHz by Greg Roberts. It was
launched into an elliptical, polar, nearly sun-synchronous
earth orbit and decayed on September 25th
1975. Recorded on September 7th
1975 on 137.290 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|

|
ANS
#07427
(1974-070A) |
 ANS (Astronomical
Netherlands Satellite) was an earth-orbiting, sun-synchronous
satellite, designed as an astronomical observatory.
Its lifetime was 20 months. Recorded on 137.890 MHz
using an SSB receiver on October 30th
1974 by Greg Roberts. ANS (Astronomical
Netherlands Satellite) was an earth-orbiting, sun-synchronous
satellite, designed as an astronomical observatory.
Its lifetime was 20 months. Recorded on 137.890 MHz
using an SSB receiver on October 30th
1974 by Greg Roberts.
|
Aug 30th
1974 |
130 kg |
 Recorded
on June 7th 1975 on 137.890
MHz in CW by Greg Roberts. Recorded
on June 7th 1975 on 137.890
MHz in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
  Both
files recorded on June 7th
1975 on 137.890 MHz in AM and CW by Greg Roberts. Both
files recorded on June 7th
1975 on 137.890 MHz in AM and CW by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Intasat
#07531
(1974-089C) |
 Intasat
was launched together with Oscar 7 and NOAA-4. This
first Spanish satellite was a small, magnetically oriented,
spin stabilized spacecraft carrying a beacon experiment
to study the ionosphere. It was turned off after 2 years.
Recorded in AM mode on September 1st
1975 on 136.710 MHz by Greg Roberts. Intasat
was launched together with Oscar 7 and NOAA-4. This
first Spanish satellite was a small, magnetically oriented,
spin stabilized spacecraft carrying a beacon experiment
to study the ionosphere. It was turned off after 2 years.
Recorded in AM mode on September 1st
1975 on 136.710 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Nov 15th
1974 |
20.4 kg |

|
CASTOR
D5B
#07802
(1975-039B) |
  CASTOR's
primary mission objective was to study the upper atmosphere
density variations. Secondary objectives included a
study of gravity field perturbations and a study of
micro-meteorite impacts. It decayed on February 18th
1979. Both files recorded on 136.240 MHz on June 21st
1975 in CW by Greg Roberts. CASTOR's
primary mission objective was to study the upper atmosphere
density variations. Secondary objectives included a
study of gravity field perturbations and a study of
micro-meteorite impacts. It decayed on February 18th
1979. Both files recorded on 136.240 MHz on June 21st
1975 in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
May 17th
1975 |
76 kg |
  Both
files recorded on June 21st
1975 on 136.240 MHz in FM by Greg Roberts. Both
files recorded on June 21st
1975 on 136.240 MHz in FM by Greg Roberts.
|
 Recorded
in AM mode on September 1st
1975 on 136.250 MHz by Greg Roberts. Recorded
in AM mode on September 1st
1975 on 136.250 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|

|
OSO-8
#07970
(1975-057A) |
 OSO-8
was supposed to perform solar physics experiments above
the atmosphere during a complete solar cycle and to
map the entire celestial sphere for direction and intensity
of UV light, X-ray radiation, and gamma-ray radiation.
Unfortunately it went out of service in September 1978
and decayed on July 9th 1986.
Recorded by Greg Roberts on 136.920 MHz in CW on June
21st 1975 just 1 hour after
its launch. OSO-8
was supposed to perform solar physics experiments above
the atmosphere during a complete solar cycle and to
map the entire celestial sphere for direction and intensity
of UV light, X-ray radiation, and gamma-ray radiation.
Unfortunately it went out of service in September 1978
and decayed on July 9th 1986.
Recorded by Greg Roberts on 136.920 MHz in CW on June
21st 1975 just 1 hour after
its launch.
|
June 21st
1975 |
1064 kg |
 Recorded
on June 21st 1975 in AM just
1 hour after its launch by Greg Roberts. Recorded
on June 21st 1975 in AM just
1 hour after its launch by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Meteor
2-01
#08026
(1975-064A) |
  Meteor
2-01 was recorded twice in the 137 MHz band in FM on
November 7th 1975 by Greg Roberts. Meteor
2-01 was recorded twice in the 137 MHz band in FM on
November 7th 1975 by Greg Roberts.
|
Jul 11th
1975 |
2800 kg |
  Meteor
2-01 was recorded also twice in the 137 MHz band in
FM in the afternoon of June 6th
1998 by DD1US. Meteor
2-01 was recorded also twice in the 137 MHz band in
FM in the afternoon of June 6th
1998 by DD1US.
|
 Click
on the picture on the right to access a collection of
APT pictures received from Meteor 2-1 in 1998 by DD1US. Click
on the picture on the right to access a collection of
APT pictures received from Meteor 2-1 in 1998 by DD1US.
|

|
COS B
#08062
(1975-072A) |
  COS B
(Cosmic Ray Satellite) was a scientific satellite developed
by the European Space Agency (ESA) to study extraterrestrial
gamma radiation in the 25-MeV to 1-GeV energy range
from a highly elliptical orbit. Recorded twice in CW/AM
mode on September 2nd 1975
on 136.950 MHz by Greg Roberts. COS B
(Cosmic Ray Satellite) was a scientific satellite developed
by the European Space Agency (ESA) to study extraterrestrial
gamma radiation in the 25-MeV to 1-GeV energy range
from a highly elliptical orbit. Recorded twice in CW/AM
mode on September 2nd 1975
on 136.950 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Aug 9th
1975 |
277.5 kg |

|
Symphonie-B
Symphonie 2
#08132
(1975-077A) |
 Symphonie
2 was a French-German, geostationary, equatorial experimental
communications satellite. It provided 1200 telephone
circuits and eight voice and two color TV channels which
operate between 4 and 6 GHz. Recorded on August 29th
1975 on 136.800 MHz by Greg Roberts. Symphonie
2 was a French-German, geostationary, equatorial experimental
communications satellite. It provided 1200 telephone
circuits and eight voice and two color TV channels which
operate between 4 and 6 GHz. Recorded on August 29th
1975 on 136.800 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Aug 27th
1975 |
400 kg |

|
D-2B Aura
#08332
(1975-092A) |
  The French
Astronomy Satellite D2B carried an EUV experiment for
solar and atmospheric investigations and a set of UV
experiments for making stellar, zodiacal light, integrated
sky background and stellar observations. The data transmission
rate was 256 b/s for real-time data and 11 kb/s for
stored data at a telemetry frequency of 136.740 MHz.
The stabilization system failed on December 28th
1976, thereby terminating operation of the spacecraft.
Recorded on October 6th 1975
in CW/AM on 136.740 MHz by Greg Roberts. The French
Astronomy Satellite D2B carried an EUV experiment for
solar and atmospheric investigations and a set of UV
experiments for making stellar, zodiacal light, integrated
sky background and stellar observations. The data transmission
rate was 256 b/s for real-time data and 11 kb/s for
stored data at a telemetry frequency of 136.740 MHz.
The stabilization system failed on December 28th
1976, thereby terminating operation of the spacecraft.
Recorded on October 6th 1975
in CW/AM on 136.740 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Sep 27th
1975 |
115 kg |

|
Meteor 2-02
#09661
(1977-002A) |
Meteor 2-02 was a  meteorological
satellite transmitting APT on 137.300 MHz (5W). Picture
received at or before December 30th
1992 by DD1US. meteorological
satellite transmitting APT on 137.300 MHz (5W). Picture
received at or before December 30th
1992 by DD1US.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to  |
Jan 7th
1977 |
2800 kg |

|
GOES 3
#10953
(1978-062A) |
GOES 3, known as GOES-C
before becoming operational, is an American geostationary
weather and communications satellite. It was originally
built for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
as part of the Geostationary Operational Environmental
Satellite system, and was launched in June 1978. It
is positioned in geostationary orbit, from where it
was initially used for weather forecasting in the United
States. Since ceasing to function as a weather satellite
in 1989, it has been used as a communications satellite,
and having spent over thirty one years in operation,
it is one of the oldest functioning satellites in orbit.
Especially the Amundsen-Scott Station at the South Pole
is using the 1.5 MBit/s link for voice and data. |
Jun 16th
1978 |
294 kg |
 GOES 3
VHF telemetry downlink was received on 136.380 MHz in
SSB on October 3rd 2013 at
23:27 UTC by Raydel CM2ESP in Havanna/Cuba. Raydel used
a horizontal Moxon antenna fixed pointed to Zenith and
a RTL-SDR Dongle with a 35dB preamplifier. Recording
kindly provided by Raydel CM2ESP. GOES 3
VHF telemetry downlink was received on 136.380 MHz in
SSB on October 3rd 2013 at
23:27 UTC by Raydel CM2ESP in Havanna/Cuba. Raydel used
a horizontal Moxon antenna fixed pointed to Zenith and
a RTL-SDR Dongle with a 35dB preamplifier. Recording
kindly provided by Raydel CM2ESP.
|

|
Cosmos 1241
Istrebitel
Sputnikov
IS
#12149
(1981-006A) |
Cosmos
1241 was a Soviet DS-P1-M target satellite launched
from the Plesetsk cosmodrome aboard a Kosmos rocket.
It was an ASAT (anti-satellite) target for the Cosmos
1243 and 1258 interceptors.
It was designated the
IS ("Istrebitel Sputnikov", fighter satellite).
The orbital parameters of the target satellite would
already be known before launch, and the interceptor
would be pre-programmed with those parameters. After
being placed into an initial parking orbit by the launch
vehicle, the interceptor's engine would make a number
of maneuvers to intercept with the target, and at the
appropriate moment, blow itself up together with the
target. The interception was intended to take place
on the first to third orbit, although it would be possible
to make repeated attempts in case the target was missed.
The Istrebitel Sputnikov was approximately spherical
in form and had a total mass of 1,400 kg. It consisted
of two sections: the main section, which contained the
guidance and targeting, computational and optical homing
systems, and the 300 kg explosive charge; and the engine
section. The body of the interceptor was designed so
that after the explosion it would fragment into 12 groups
of shrapnel. The specified radius of guaranteed target
destruction was 1 km. However in a head-on intercept,
only 400 m radius was guaranteed, while in a chase intercept,
a 2 km radius of destruction could be achieved. The
engine was capable of numerous quick starts and restarts,
with a total operating time of 300 seconds. |
Jan 21st
1981 |
650 kg |
 This signal
of the Anti-Satellite Test (ASAT) target was received
on 145 MHz on February 2nd
1981 by Sven Grahn. This signal
of the Anti-Satellite Test (ASAT) target was received
on 145 MHz on February 2nd
1981 by Sven Grahn.
|

|
COSMOS 1249
US-A
RORSAT
#12319
(1981-021A) |
Cosmos 1249 was a russian
nuclear powered Radar Ocean Reconnaissance Satellite
(RORSAT) launched from the Baikonur cosmodrome aboard
a Tsyklon 2 rocket. The Russian name for this series
of satellites was Upravlenniye Sputnik Aktivny (US-A).
The RORSATs were designed to search the oceans for US
Navy task forces and other shipping using a side-looking
radar operating at 8.2 GHz. These highly maneuverable
satellites had a orbit with an inclination of about
65° which was initially about 255 high (LEO) and
after the nuclear reactor degraded in power the orbit
was raised to a about 900km circular disposal orbit
(MEO). Cosmos-1249 operated 105 days in the LEO
orbit. |
Mar 5th
1981 |
3800 kg |
 Enclosed
FSK, PDM signal was received on 19.542 MHz on April
26th 1981 at 07:00 UTC by Sven
Grahn. Enclosed
FSK, PDM signal was received on 19.542 MHz on April
26th 1981 at 07:00 UTC by Sven
Grahn.
|

|
COSMOS 1266
US-A
RORSAT
#12409
(1981-037A) |
Cosmos 1266 was a russian
nuclear powered Radar Ocean Reconnaissance Satellite
(RORSAT) launched from the Baikonur cosmodrome aboard
a Tsyklon 2 rocket. COSMOS-1266 was the tandem satellite
to COSMOS-1249 and stayed only 8 days in LEO orbit.
More information on the RORSAT/US-A satellites can be
found on the excellent website of Sven Grahn. |
Apr 21st
1981 |
3800 kg |
 Enclosed
“pulsed” FSK/PDM signal was received on 19.542 MHz on
May 2nd 1981 at 04:10 UTC by
Sven Grahn . Enclosed
“pulsed” FSK/PDM signal was received on 19.542 MHz on
May 2nd 1981 at 04:10 UTC by
Sven Grahn .
|

|
Meteosat
2
#12554
(1981-057A) |
 Meteosat-2
was a spin-stabilized cylindrical meteorological satellite
in a geostationary orbit at 0° longitude. It transmitted
weather pictures on the downlink frequencies 1691.0
MHz and 1694.5 MHz. Recorded in FM by Greg Roberts. Meteosat-2
was a spin-stabilized cylindrical meteorological satellite
in a geostationary orbit at 0° longitude. It transmitted
weather pictures on the downlink frequencies 1691.0
MHz and 1694.5 MHz. Recorded in FM by Greg Roberts.
|
Jun 19th
1981 |
282 kg |

|
Lansat
5
Landsat-D1
#14780
(1984-021A) |
The Landsat
5 satellite was identical to Landsat 4. This experimental
earth resources monitoring system featured new powerful
remote-sensing capabilities (incl. higher resolution
and data rate) of the  thematic
mapper (TM). It had a complete end-to-end highly automated
new generation data system which was a major step
forward in global remote-sensing applications. The spectrum
plot of the S-band downlink at 2287.5 MHz was recorded
on February 26th 2012 at 05:37UTC
by Loren WA7SKT. thematic
mapper (TM). It had a complete end-to-end highly automated
new generation data system which was a major step
forward in global remote-sensing applications. The spectrum
plot of the S-band downlink at 2287.5 MHz was recorded
on February 26th 2012 at 05:37UTC
by Loren WA7SKT. |
Mar 1st
1984 |
1407 kg |

|
NOAA 9
NOAA-F
#15427
(1984-123A) |
NOAA-9 was also called
NOAA-F.  APT
downlink frequency was 137.620 MHz (inoperative), HRPT
downlink frequencies were 1702.5 MHz and 1707.0 MHz,
Beacon frequency was 137.770 MHz (on command). Picture
received at or before December 30th
1992 by DD1US. APT
downlink frequency was 137.620 MHz (inoperative), HRPT
downlink frequencies were 1702.5 MHz and 1707.0 MHz,
Beacon frequency was 137.770 MHz (on command). Picture
received at or before December 30th
1992 by DD1US. |
Dec 12th
1984 |
1418 kg |
 On November
6th 2010 at 15:22h UTC NOAA-9
transmitted a plain CW carrier on the downlink frequency
137.504 MHz. Received, recorded and kindly provided
by Patrick Hajagos. On November
6th 2010 at 15:22h UTC NOAA-9
transmitted a plain CW carrier on the downlink frequency
137.504 MHz. Received, recorded and kindly provided
by Patrick Hajagos.
|

|
AUSSAT-1
AUSSAT A1
OPTUS-A1
#15993
(1985-076B) |
Aussat 1 was released
from the Space Shuttle on August 29th
1985. This spacecraft was Australia's first dedicated
communications spacecraft. It was a Hughes HS-376 satellite,
and it operated with extremely tight pointing accuracies
using a new triple dish spot beam antenna designed specifically
for Australia. It provided the first continuous television
and radio facility to thousands of remote Australian
homesteads and communities. It also provided a real-time
communications relay for Australian air traffic control,
receiving aircraft signals relayed from VHF grand stations.
The satellite was spin-stabilized and ejected from the
payload bay attached to a PAM perigee kick stage. The
satellite operated at the 14/12 GHz Ku band, with an
effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) of 47 dBW
for the spot beams and 36 dBW for FSS. |
Aug 29th
1985 |
655 kg |
 This recording
was made during the release of Aussat from the Space
Shuttle. It is part of the compilation "The Conquest
of Space" of the Astronautical Society of Western
Australia and kindly provided by Jos Heymann. This recording
was made during the release of Aussat from the Space
Shuttle. It is part of the compilation "The Conquest
of Space" of the Astronautical Society of Western
Australia and kindly provided by Jos Heymann.
|

|
COSMOS
1766
OKEAN-O1 #1
#16881
(1986-055A) |
   Cosmos
1766 was an oceanographic satellite equipped with optical
scanners and radar imaging devices. Recorded on 137.400
MHz in FM by Greg Roberts. Cosmos
1766 was an oceanographic satellite equipped with optical
scanners and radar imaging devices. Recorded on 137.400
MHz in FM by Greg Roberts.
|
Jun
28th 1986 |
1950
kg |
 Enclosed
signal of an image transmission was received on 466.5
MHz on January 7th 1990 by
Sven Grahn. Enclosed
signal of an image transmission was received on 466.5
MHz on January 7th 1990 by
Sven Grahn.
|

|
NOAA 10
NOAA-G
#16969
(1986-073A) |
NOAA-10 was also called
NOAA-G and
included a search and rescue (SAR) system. Its primary
purpose was meteorological though. APT downlink frequency
is 137.500 MHz, HRPT downlink frequency is 1698.0 MHz,
Beacon frequency is 136.770 MHz. Picture received at
or before December 30th 1992
by DD1US. and
included a search and rescue (SAR) system. Its primary
purpose was meteorological though. APT downlink frequency
is 137.500 MHz, HRPT downlink frequency is 1698.0 MHz,
Beacon frequency is 136.770 MHz. Picture received at
or before December 30th 1992
by DD1US. |
Sep 17th
1986 |
386 kg |
I am searching for sound
files. Please send them to  |

|
ECS-4
EUTELSAT 4
#18351
(1987-078B) |
 The EUTELSAT
I series of satellites was developed by the European
Space Agency (ESA) as part of the European Communications
Satellite (ECS) program. They served both public and
private traffic, including telephone services, fax,
data, land mobile service, and television and radio
programming. PCM/FSK/PM transmission recorded on 137.142
MHz by Mike D. Kenny. The EUTELSAT
I series of satellites was developed by the European
Space Agency (ESA) as part of the European Communications
Satellite (ECS) program. They served both public and
private traffic, including telephone services, fax,
data, land mobile service, and television and radio
programming. PCM/FSK/PM transmission recorded on 137.142
MHz by Mike D. Kenny.
|
Sep 16th
1987 |
1175 kg |

|
Navigation satellite OSCAR-27
Transit-O 27
OSCAR(NAV)27
NNS 30270
#18361
(1987-080A) |
 Transit-O
27 was a US Navy navigation satellite launched by a
Scout G rocket. Transit, one of the first operational
satellite systems, was also known as the Navy Navigation
Satellite (NNS). Transit-O
27 was a US Navy navigation satellite launched by a
Scout G rocket. Transit, one of the first operational
satellite systems, was also known as the Navy Navigation
Satellite (NNS).
The Transit spacecraft were developed
for updating the inertial navigation systems on board
US Navy Polaris submarines, and later for civilian use.
Transit receivers used the known characteristics of
the satellite's orbit, measured the Doppler shift of
the satellite's radio signal, and thereby calculated
the receivers position on the earth. As a single spacecraft
travelled overhead, the user measured the Doppler shift
over a 15 minute period by receiving timing marks and
satellite orbital information on two separate frequencies,
149.99 and 399.97 MHz. These signals were corrected
for ionospheric refraction and the information was then
fed into the users navigation system.
Individual
Transit satellites operated for over 10 years. Technical
breakthroughs during the program included gravity gradient
stabilization, the use of radio-isotope thermoelectric
generators (RTG), and navigation satellite technologies
later used in the GPS system. Transit was superseded
by the Navstar global positioning system. The use of
the satellites for navigation was discontinued at the
end of 1996 but the satellites continued transmitting
and became the Navy Ionospheric Monitoring System (NIMS).
Enclosed signal was received on 149.985 MHz on January
15th 2000 by Sven Grahn.
|
Sep 16th
1987 |
59 kg |

|
NOSS 9
USA 32
P-11 5103
#19460
(1988-078A) |
US Navy Ocean Surveillance
Satellite 9 (NOSS 9) was launched from Vandenberg AFB
aboard an Titan-2(23)G rocket into a near-circular 790 km
orbit with 85° inclination. It placed a cluster
of one primary satellite and three smaller sub-satellites
(that trailed along at distances of several hundred
kilometers) into low polar orbit. This satellite array
determined the location of radio and radars transmitters,
using triangulation, and the identity of naval units,
by analysis of the operating frequencies and transmission
patterns. |
Sep 5th
1988 |
1700 kg |
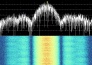 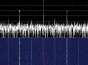  NOSS 9
has multiple S-band downlinks around 2202 MHz. USA 32
was received on May 10th 2013
at 09:50 UTC by Paul Marsh. Spectrum plots and audio
recording kindly provided by Paul Marsh M0YET. NOSS 9
has multiple S-band downlinks around 2202 MHz. USA 32
was received on May 10th 2013
at 09:50 UTC by Paul Marsh. Spectrum plots and audio
recording kindly provided by Paul Marsh M0YET.
|

|
NOAA 11
NOAA-H
#19531
(1988-089A) |
NOAA-11 was also called
NOAA-H.  APT
downlink frequency is 137.620 MHz, HRPT downlink frequency
is 1707.0 MHz, Beacon frequency is 137.770 MHz. Picture
received at or before Dec 31st
1992 by DD1US. APT
downlink frequency is 137.620 MHz, HRPT downlink frequency
is 1707.0 MHz, Beacon frequency is 137.770 MHz. Picture
received at or before Dec 31st
1992 by DD1US.
I am searching for sound files. Please
send them to  |
Sep 24th
1988 |
386 kg |

|
AKEBONO
EXOS-D
#19822
(1989-016A) |
The purpose of this
Japanese mission was to investigate the particle acceleration
regions above the auroral region in order to develop
a better understanding of the acceleration mechanism
and of its relation to substorm phenomena. The spacecraft
was spin-stabilized with a rotation rate of 7.5 rpm.
The attitude was magnetically controlled with spacecraft
axis pointing to the sun. The satellite control and
main telemetry station is at Kagoshima. |
Feb 21st
1989 |
294 kg |
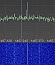 The
S-Band downlink on 2280.5 MHz of Akebono was received
and enclosed FFT plot was generated in April 2014 by
Milen Rangelov. The
S-Band downlink on 2280.5 MHz of Akebono was received
and enclosed FFT plot was generated in April 2014 by
Milen Rangelov.
|

|
FLTSATCOM
8
USA 046
#20253
(1989-077A) |
 FLTSATCOM
8 (Fleetsatcom) is a geostationary (23°W) military
communications satellite. It has 23 communications channels
in the UHF frequency band from 244 to 263 MHz. Sometimes
some of the channels get hijacked by pirates and used
for private purpose. Such an event was recorded on on
Jan 5th 2008 on 255.550 MHz
in NFM by Chris Gross in Pennsylvania using a Yupiteru
MVT-7100. FLTSATCOM
8 (Fleetsatcom) is a geostationary (23°W) military
communications satellite. It has 23 communications channels
in the UHF frequency band from 244 to 263 MHz. Sometimes
some of the channels get hijacked by pirates and used
for private purpose. Such an event was recorded on on
Jan 5th 2008 on 255.550 MHz
in NFM by Chris Gross in Pennsylvania using a Yupiteru
MVT-7100.
|
Sep 25th
1989 |
1043 kg |
 Another
example for a pirate signal was recorded on 255.550
MHz on Dec 16th 2006 in NFM by Chris Gross in Pennsylvania
using a Yupiteru MVT-7100. Another
example for a pirate signal was recorded on 255.550
MHz on Dec 16th 2006 in NFM by Chris Gross in Pennsylvania
using a Yupiteru MVT-7100.
|

|
NAVSTAR
22
Navstar-2A 1
GPS 23
USA 66
#20959
(1990-103A) |
NAVSTAR GPS (global positioning
system) satellite of the 2nd
generation. These type IIA navigation satellites are
orbiting the Earth in an altitude of 20000 km with an
inclination of 55°. The L1 (for civilian and military
use) downlink frequency is 1575.42 MHz, the L2 (only
for military use) downlink frequency is 1227.60 MHz. |
Nov 26th
1990 |
1816 kg |
 Enclosed
GPS signal was received on April 7th
2011 on 1575,42 MHz in SSB by Greg Roberts. Enclosed
GPS signal was received on April 7th
2011 on 1575,42 MHz in SSB by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Meteor 3-4
#21232
(1991-030A) |
Meteor 3-4 transmitted
APT on  137.???
MHz. Picture received at or before Dec 30th
1992 by DD1US. 137.???
MHz. Picture received at or before Dec 30th
1992 by DD1US. |
Apr 24th
1991 |
2150 kg |

|
NOAA
12
NOAA-D
#21263
(1991-032A) |
 NOAA-12
was also called NOAA-D. APT downlink frequency is 137.500
MHz, HRPT downlink frequency is 1698.0 MHz, Beacon frequency
is 136.770 MHz. NOAA 12 was de-commissioned (permanently
switched off) on 10 August 2007 after more than 16 years
of service. Received on May 5th
1998 by DD1US. NOAA-12
was also called NOAA-D. APT downlink frequency is 137.500
MHz, HRPT downlink frequency is 1698.0 MHz, Beacon frequency
is 136.770 MHz. NOAA 12 was de-commissioned (permanently
switched off) on 10 August 2007 after more than 16 years
of service. Received on May 5th
1998 by DD1US.
|
May
14th 1991 |
590
kg |
 In
the year 1998 I received a number of APT pictures from
NOAA-12. Click on the picture on the right to have a
look at this collection. In
the year 1998 I received a number of APT pictures from
NOAA-12. Click on the picture on the right to have a
look at this collection.
|

|
TUBSAT-A
#21577
(1991-050D) |
Tubsat-A (Technische
Universität Berlin Satellite) was a cube of 38cm
length and launched together with ERS1 on an Ariane-4
from Kourou into a sun-synchronous polar orbit with
an inclination of 98 degree and a height of 780km. TUBSAT-A
transmitted telemetry (including 12 temperature and
20 voltage values) and command data on 143.075 MHz in
1200bd FFSK raw binary ASCII. |
July
17th 1991 |
35
kg |
  Enclosed
signal was received in May 2006 Enclosed
signal was received in May 2006
in FM on 143.075
MHz by Maik . You can also download the decoded binary
file when clicking on the icon in the upper right. The
header is "UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU
UUUUTUBSAT Communication Unit..Technischd
Universitaet
Berlin..Institut fuer Raumfahrttechnik..
Base Data
System…".
Recording kindly provided
by Maik Hermenau.
|

|
Meteor
3-5
TOMS
#21655
(1991-056A) |
 Cooperative
space mission between the US and the former USSR to
map global ozone from space using a Total Ozone Mapping
Spectrometer (TOMS) designed and operated by NASA. Meteor
3-5 transmitted APT on 137.850 MHz. Received on May
1st 1998 by DD1US. Cooperative
space mission between the US and the former USSR to
map global ozone from space using a Total Ozone Mapping
Spectrometer (TOMS) designed and operated by NASA. Meteor
3-5 transmitted APT on 137.850 MHz. Received on May
1st 1998 by DD1US.
|
Aug
15th 1991 |
2150
kg |
 In
the year 1998 I received a number of APT pictures from
Meteor 3-5. Click on the picture on the right to have
a look at this collection. Audio recorded on May 1st
1998 by DD1US. In
the year 1998 I received a number of APT pictures from
Meteor 3-5. Click on the picture on the right to have
a look at this collection. Audio recorded on May 1st
1998 by DD1US.
|

|
COSMOS
2184
#21937
(1992-020A) |
 Cosmos
2184 was part of a 6-satellite Russian military navigation
system distributed in orbital planes spaced 30 degrees
apart and launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome aboard
a Cosmos rocket. Navigation information was derived
from Doppler-shifted VHF transmissions (approximately
150 and 400 MHz) of the satellite position and orbital
data. Recorded on Dec 16th 2006 on 149.910 MHz by Chris
Gross in Pennsylvania using a Yupiteru MVT-7100. Cosmos
2184 was part of a 6-satellite Russian military navigation
system distributed in orbital planes spaced 30 degrees
apart and launched from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome aboard
a Cosmos rocket. Navigation information was derived
from Doppler-shifted VHF transmissions (approximately
150 and 400 MHz) of the satellite position and orbital
data. Recorded on Dec 16th 2006 on 149.910 MHz by Chris
Gross in Pennsylvania using a Yupiteru MVT-7100.
|
Apr 15th
1992 |
825 kg |

|
HealthSat-2
Healthsat-II
WavSat-1
#22827
(1993-061E) |
Healtsat-2
joined HealthSat-1 (UoSAT-3) as secondary microsatellite
in the HealthNet system of SatelLife. It was build by
SSTL in Surrey/UK based on its MicroSat-70 platform
and launched together with the primary payload SPOT-3
and several other microsats into a LEO (low earth orbit)
on Ariane 40 V59 from Kourou. This store and forward
communications satellite provides a communications network
especially for remote regions. For instance it relays
medical emergency information from Africa to hospitals
and health documentation centers. HealthSat-2 feature
3 uplink receivers at VHF and 2 redundant downlink transmitters
at UHF. It uses omni-directional satellite antennas.
The modulation and data rate is switchable between 1200bd
AFSK and 9600bd FSK in the uplink and 9600bd FSK and
38400 bps FSK in the downlink. It uses the AX.25 packet
communications protocol developed for Amateur Radio.
The output power of the transmitter is adapted by computer
control between 1W and 10W. Under a unique partnership
agreement between Wavix, SatelLife, and VITA, the satellite
under the name WavSat-1 continues its humitarian mission.
|
Sep 26th
1993 |
48 kg |

|
NAVSTAR
35
Navstar 2A-14
GPS 2-23
USA 96
#22877
(1993-068A) |
NAVSTAR GPS (global positioning
system) satellite of the 2nd
generation. These type IIA navigation satellites are
orbiting the Earth in an altitude of 20200 km with an
inclination of 55°. The L1 (for civilian and military
use) downlink frequency is 1575.42 MHz, the L2 (only
for military use) downlink frequency is 1227.60 MHz. |
Oct 26th
1993 |
840 kg |
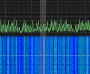  Enclosed
GPS signal of NAVSTAR 35 was received on May lst
2011 on 1575,4 MHz in SSB by Greg Roberts. Enclosed
GPS signal of NAVSTAR 35 was received on May lst
2011 on 1575,4 MHz in SSB by Greg Roberts.
|

|
OKEAN
4 (1-7)
#23317
(1994-066A) |
 Okean
4 (1-7) was a Russian / Okean
4 (1-7) was a Russian /  Ukrainian
oceanic / meteorological satellite. It transmitted on
137.400 MHz. Picture received on March 21st
1998 by DD1US. The enclosed audio file recorded on 137.400
MHz was kindly provided by Mike DK3WN. Ukrainian
oceanic / meteorological satellite. It transmitted on
137.400 MHz. Picture received on March 21st
1998 by DD1US. The enclosed audio file recorded on 137.400
MHz was kindly provided by Mike DK3WN.
|
Oct 11th
1994 |
1950 kg |

|
NOAA 14
#23455
(1994-089A) |
 Besides
an imaging radiometer, NOAA 14 (also called NOAA-J)
carried optical sounders to monitor temperature and
moisture content in the atmosphere, and counters to
measure energetic electrons and protons. APT downlink
frequency is 137.620 MHz, HRPT downlink frequency is
1698.0 MHz, Beacon frequency is 136.770 MHz. The audio
file was recorded on March 8th
1998 by DD1US. Besides
an imaging radiometer, NOAA 14 (also called NOAA-J)
carried optical sounders to monitor temperature and
moisture content in the atmosphere, and counters to
measure energetic electrons and protons. APT downlink
frequency is 137.620 MHz, HRPT downlink frequency is
1698.0 MHz, Beacon frequency is 136.770 MHz. The audio
file was recorded on March 8th
1998 by DD1US.
|
Dec 30th
1994 |
1421 kg |
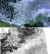 The
picture on the right was received on March 1st
1998 by DD1US and shows a comparison of the APT picture
received on 137.620 MHz to the HRPT picture (derived
from the internet). The
picture on the right was received on March 1st
1998 by DD1US and shows a comparison of the APT picture
received on 137.620 MHz to the HRPT picture (derived
from the internet).
|
 In
the year 1998 I received a number of APT pictures from
NOAA 14. Click on the second picture on the right to
have a look at this collection. In
the year 1998 I received a number of APT pictures from
NOAA 14. Click on the second picture on the right to
have a look at this collection.
|

|
ERS-2
ERS 2
#23560
(1995-021A) |
ERS 2 is an ESA
earth resources spacecraft launched by an Ariane rocket
from the Kourou Space Center in French Guiana. The spacecraft
carries a synthetic aperture radar for topographic studies,
a wide beam radar (both in the C-band), a radar altimeter
for measuring ocean surface and waves, a radiometer
for measuring ocean surface temperatures, and an optical
Global Ozone Monitor (GOME) that monitors ozone and
ozone-destroying gases and carries reflectors for laser
tracking. It has a 6.5 gigabit tape recorder to record
data from a full orbit. |
Apr
21st 1995 |
2516 kg |
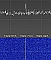 The
S-Band downlink on 2225 MHz of ERS-2 was received and
enclosed FFT plot was generated in May 2014 by Milen
Rangelov. The
S-Band downlink on 2225 MHz of ERS-2 was received and
enclosed FFT plot was generated in May 2014 by Milen
Rangelov.
|

|
SICH-1
#23657
(1995-046A) |
 SICH-1
offered RADAR and thermal microwave imagery in addition
to the more usual visible light transmissions. Resolution
was approx. 1 km. SICH-1 transmitted APT on 137.400
MHz and higher resolution pictures at 465 MHz. The enclosed
audio file recorded on 137.400 MHz was kindly provided
by Mike DK3WN. SICH-1
offered RADAR and thermal microwave imagery in addition
to the more usual visible light transmissions. Resolution
was approx. 1 km. SICH-1 transmitted APT on 137.400
MHz and higher resolution pictures at 465 MHz. The enclosed
audio file recorded on 137.400 MHz was kindly provided
by Mike DK3WN.
 The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark B. The
APT signal was decoded and kindly provided by Mark B.
|
Aug 31st
1995 |
1950 kg |
Picture |
Object
name
#NORAD |
Description |
Launch
Date |
Weight |