Picture |
Object
name
#NORAD |
Description |
Launch
Date |
Weight |

|
TIROS-4
A 9
TIROS-D
1962-Beta-1
#00226
(1962-002A) |
TIROS 4 (Television and
InfraRed Observation Satellite) was a meteorogical satellite
and launched on an Delta DM-19 rocket from Cape Canaveral. |
Feb
8th 1962 |
129
kg |
 Enclosed
signal of TIROS-D during its orbit #1782 was received
on June 12th 1962 by Volkssternwarte
Munich, also called "Satellitenbeobachtungsstation
Munich II". The signal was received on 136.23 MHz.
TIROS-4 was the first of its series to use a 136 MHz
instead of the previously used 108 MHZ. There is an
additional time pulse signal inserted in the recording
which was kindly provided by Tobias Lindemann and Josef
Huber. Enclosed
signal of TIROS-D during its orbit #1782 was received
on June 12th 1962 by Volkssternwarte
Munich, also called "Satellitenbeobachtungsstation
Munich II". The signal was received on 136.23 MHz.
TIROS-4 was the first of its series to use a 136 MHz
instead of the previously used 108 MHZ. There is an
additional time pulse signal inserted in the recording
which was kindly provided by Tobias Lindemann and Josef
Huber.
|
 This recording
is from vinyl no. 39which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini This recording
is from vinyl no. 39which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini
|


|
OSO
1
S 16
#00255
(1962-006A) |
OSO 1 (Orbiting Solar
Observatory) was launched from Cape Canaveral into a
550kmx595km orbit with an inclination of 32.85°.
It was the first satellite to have pointed instruments
and onboard tape recorders for data storage. OSO 1 transmitted
data on 136.744 MHz on 75 solar flares until August
6th 1963. It decayed on October
8th 1981. |
Mar
7th 1962 |
207.7
kg |
 This recording
of OSO 1 was done from Heinz Kaminski at Observatorium
Bochum/Germany and is from vinyl no. 43 which was included
in the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The
man and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini This recording
of OSO 1 was done from Heinz Kaminski at Observatorium
Bochum/Germany and is from vinyl no. 43 which was included
in the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The
man and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini
|

|
KOSMOS
1
COSMOS 1
DS-2
Sputnik 11
#00266
(1962-008A) |
DS-2 (Dnepropetrovsk
Sputnik 2) is the second development version of the
Denpropetrovsk Sputnik series. After two unsuccessful
launches of the DS-1 satellite, the simplified DS-2
satellite, which omitted the central cylindrical section
for mission avionics, was successfully launched on March
16th 1962. After reaching orbit
it received the designator KOSMOS 1. It employed radio
methods to study the structure of the ionosphere. It
transmitted on 20.006 MHz and 90.027 MHz. It decayed
on May 25th 1962. |
March 16th
1962 |
47 kg |
 This recording
is from vinyl no. 42 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Cosmos 1 was received
by the observatory in Bochum. Digitized and kindly provided
by Federico Manzini This recording
is from vinyl no. 42 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Cosmos 1 was received
by the observatory in Bochum. Digitized and kindly provided
by Federico Manzini
|

|
KOSMOS
2
COSMOS 2
1MS
Sputnik 12
#00269
(1962-009A) |
The 1MS series were prototypes
of small battery powered research satellites. The objective
was to test systems for future satellites and to record
data about cosmic radiation. After its successful launch
it got the designator KOSMOS-2. It decayed on October
25th 1962. |
April 6th
1962 |
285 kg |
I am searching for sound
files. Please send them to
 |

|
Ariel
1
UK 1
S 51
1962-Omicron-1
#00285
(1962-015A) |
Ariel 1 was built and
operated by UK and launched on an American Thor-Delta
rocket from Cape Canaveral. Ariel 1
was designed to contribute to the current knowledge
of the ionosphere and of sun-ionosphere relationships.
The satellite was a 62 kg cylinder with a 58-cm diameter
and a height of 22 cm. It decayed on April 24th
1976. |
April
26th 1962 |
62
kg |
 Enclosed
signal was received on June 12th
1962 at 16:42 UTC by Volkssternwarte Munich which was
also called "Satellitenbeobachtungsstation Munich
II". The signal was received on 136.408 MHz. There
is an additional time pulse signal inserted in the recording
which was kindly provided by Tobias Lindemann and Josef
Huber. Enclosed
signal was received on June 12th
1962 at 16:42 UTC by Volkssternwarte Munich which was
also called "Satellitenbeobachtungsstation Munich
II". The signal was received on 136.408 MHz. There
is an additional time pulse signal inserted in the recording
which was kindly provided by Tobias Lindemann and Josef
Huber.
|
 Enclosed
signal was received probably on June 23rd
1962 at 02:10 UTC by Volkssternwarte Munich. Please
note that the satellite signal is the multitone signal
in the background. There is an additional time pulse
signal inserted in the recording which was kindly provided
by Tobias Lindemann and Josef Huber. Enclosed
signal was received probably on June 23rd
1962 at 02:10 UTC by Volkssternwarte Munich. Please
note that the satellite signal is the multitone signal
in the background. There is an additional time pulse
signal inserted in the recording which was kindly provided
by Tobias Lindemann and Josef Huber.
|
 This recording
of ARIEL 1 is from vinyl no. 43 which was included in
the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man
and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini. This recording
of ARIEL 1 is from vinyl no. 43 which was included in
the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man
and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini.
|
 Enclosed
signal was received by Bruce Window at Island Lagoon
Minitrack station (part of Honeysuckle Creek Tracking
Stations) and kindly provided by Colin Mackellar. Enclosed
signal was received by Bruce Window at Island Lagoon
Minitrack station (part of Honeysuckle Creek Tracking
Stations) and kindly provided by Colin Mackellar.
|

|
KOSMOS
4
COSMOS 4
Sputnik 14
#00287
(1962-014A) |
KOSMOS 4 was one of a
series of Soviet earth satellites whose purpose was
to study outer space, the upper layers of the atmosphere,
and the earth. Scientific data and measurements were
relayed to earth by multichannel telemetry systems equipped
with space-borne memory units. It transmitted on 19.995
MHz. The mission of Cosmos 4 was to measure radiation
before and after the US nuclear tests conducted during
project Starfish. The reconnaissance satellite was recovered
on April 29th 1962. |
April 26th
1962 |
4600 kg |
 COSMOS
4 was recorded by Heinz Kaminski in Bochum/Germany and
is from vinyl no. 43 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini. COSMOS
4 was recorded by Heinz Kaminski in Bochum/Germany and
is from vinyl no. 43 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini.
|

|
KOSMOS
5
COSMOS 5
2MS #2
Sputnik 15
#00297
(1962-020A) |
KOSMOS 5 was a scientific
and research satellite launched into an elliptical
low Earth orbit with an inclination of 49.1 degree and
a perigee of 192 km and a perigee of 1578 km. It decayed
on May 2nd 1963. |
May 28th
1962 |
280 kg |
 KOSMOS
5 was received on June 23rd
1962 from 18:58 until 19:17 UTC on 20.008 MHz by Volkssternwarte
Munich based in Sommerstrasse. KOSMOS
5 was received on June 23rd
1962 from 18:58 until 19:17 UTC on 20.008 MHz by Volkssternwarte
Munich based in Sommerstrasse.
|
 COSMOS
5 was also received on September 2nd
1962 at 17:42 UTC by Volkssternwarte Munich. Recording
kindly provided by Tobias Lindemann and Josef Huber. COSMOS
5 was also received on September 2nd
1962 at 17:42 UTC by Volkssternwarte Munich. Recording
kindly provided by Tobias Lindemann and Josef Huber.
|

|
TIROS-5
TIROS-E
1962-aa-1
#00309
(1962-025A) |
 TIROS-5
was a meteorological satellite. It included television
cameras and returned 58226 cloud cover photos until
May 4th 1963. It transmitted
tracking beacons on 136.230 and 136.920 Mhz. It also
featured a 5W television transmitter on 235 MHz. Signal
on 136.230 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in CW by Greg Roberts. TIROS-5
was a meteorological satellite. It included television
cameras and returned 58226 cloud cover photos until
May 4th 1963. It transmitted
tracking beacons on 136.230 and 136.920 Mhz. It also
featured a 5W television transmitter on 235 MHz. Signal
on 136.230 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
Jun
19th 1962 |
130
kg |
 Signal
on 136.920 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in CW by Greg Roberts. Signal
on 136.920 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
 Signal
on 136.920 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in AM by Greg Roberts. Signal
on 136.920 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in AM by Greg Roberts.
|
 Signal
on 136.920 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in FM by Greg Roberts. Signal
on 136.920 MHz recorded on Dec 14th
1973 in FM by Greg Roberts.
|
 Signal
on 136.230 MHz recorded on June 7th
1975 in CW by Greg Roberts. Signal
on 136.230 MHz recorded on June 7th
1975 in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
 This recording
is from vinyl no. 51 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini This recording
is from vinyl no. 51 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini
|

|
TELSTAR
1
#00340
(1962-029A) |
Telstar 1, primarily
a communications satellite providing 60 simultaneous
telephone conversations, carried an experiment designed
to measure the energetic proton and electron distribution
in the Van Allen belts. Scientific information was transmitted
by the spacecraft telemetry beacon on 136 MHz via a
PCM/FM/AM encoder. The telemetry sequence required about
1 min. Another beacon was at 4080 MHz and the communication
experiments operated on simplex (4170 MHz, 2.25 Watts)
and duplex (4165 MHz, 1 Watt and 4175 MHz, 1 Watt). |
July 10th
1962 |
171 kg |
 This recording
is from vinyl no. 46 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. It includes the signal
of the telemetry channel as well as the first phone
call via Telstar. Digitized and kindly provided by Federico
Manzini. This recording
is from vinyl no. 46 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. It includes the signal
of the telemetry channel as well as the first phone
call via Telstar. Digitized and kindly provided by Federico
Manzini.
|


|
Alouette-1
Alouette-A
1962-ßa-1
#00424
(1962-049A) |
Alouette
1 was a Canadian small ionospheric observatory instrumented
with an ionospheric sounder, a VLF receiver, an energetic
particle detector, and a cosmic noise experiment. Extended
from the satellite shell were two dipole antennas (45.7
m and 22.8 m long, respectively) which were shared by
three of the experiments on the spacecraft. Alouette-1
had a tracking beacons transmitting with 50 mWatts on
136.980 MHz and two telemetry transmitter on 136.080
MHz (2 Watts) and 136.590 MHz (0.25 Watts). |
Sept.
29th 1962 |
145
kg |
 This
recording is from vinyl no. 52 which was included in
the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man
and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini This
recording is from vinyl no. 52 which was included in
the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man
and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini
|

|
Explorer
14
EPE-B
1962-Beta-Gamma-1
#00432
(1962-051A) |
Explorer
14 was a spin-stabilized, solar-cell-powered spacecraft
launched by the USA into a highly elliptical orbit (300kmx85300km).
It measured cosmic-ray particles, trapped particles,
solar wind protons and magnetospheric and interplanetary
magnetic fields. Explorer 14 transmitted on 136 MHz
with 2 Watts until November 1963. It decayed on July
1st 1966. |
Oct
2nd 1962 |
40
kg |
 This recording
is from vinyl no. 53 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini. This recording
is from vinyl no. 53 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini.
|
 Enclosed
signal was received by Bruce Window at Island Lagoon
Minitrack station (part of Honeysuckle Creek Tracking
Stations) and kindly provided by Colin Mackellar. Enclosed
signal was received by Bruce Window at Island Lagoon
Minitrack station (part of Honeysuckle Creek Tracking
Stations) and kindly provided by Colin Mackellar.
|

|
Explorer
15
EPE-C
S 3B
#00445
(1962-059A) |
Explorer 15 was a spin-stabilized,
solar-cell-powered spacecraft instrumented to study
the artificial radiation belt produced by the Starfish
high-altitude nuclear burst of July 1962. It was part
of the Energetic Particles Explorer (EPE) series of
satellites. A 16-channel PFM/PM time-division multiplexed
telemeter was used. The time required to sample the
16 channels (one frame period) was 0.323 s. Half of
the channels were used to convey eight-level digital
information, and the others were used for analog information.
|
Oct. 27th
1962 |
44,4 kg |
 This
recording was done in Bochum/Germany and is part of
vinyl no. 56 which was included in the Italian Enciclopaedia
L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space) issued 1965
by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly provided by
Federico Manzini This
recording was done in Bochum/Germany and is part of
vinyl no. 56 which was included in the Italian Enciclopaedia
L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space) issued 1965
by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly provided by
Federico Manzini
|

|
ANNA-1B
#00446
(1962-060A) |
Anna 1B was a US Navy
geodetic satellite launched from Cape Canaveral by a
Thor Able Star rocket. |
Oct. 31st
1962 |
161 kg |
 This
recording was done in Bochum/Germany and is part of
vinyl no. 56 which was included in the Italian Enciclopaedia
L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space) issued 1965
by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly provided by
Federico Manzini This
recording was done in Bochum/Germany and is part of
vinyl no. 56 which was included in the Italian Enciclopaedia
L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space) issued 1965
by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly provided by
Federico Manzini
|

|
Injun
3
Injun 2B
#00504
(1962-067B) |
Injun 3 was
a magnetic field-aligned-spacecraft instrumented for
a study of geophysical phenomena, particularly high-latitude
and auroral, using an integrated system of several particle
detectors, a VLF detector, and three auroral photometers.
It transmitted on 136.870 MHz also "Starfish"
radiation data. Injun-3 decayed on August 25th
1968. |
Dec
13th 1962 |
52
kg |
 This recording
of Injun 3 is from vinyl no. 57 which was included in
the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man
and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini This recording
of Injun 3 is from vinyl no. 57 which was included in
the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man
and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini
|

|
Relay 1
Relay A
#00503
(1962-068A) |
Relay 1 was primarily
a communications satellite built by NASA. The spin-stabilized
spacecraft included in addition radiation experiments
designed to map the earth's radiation belts. It transmitted
on 136.140 MHz and 136.620 MHz tracking and telemetry
data with 250 mW. Further it featured a wideband transmitter
with 11 W at 4170 MHz. Finally it supported 2-way telephone
and other narrow-band traffic with the transmitters
on 4165 MHz and 4175 MHz (11 W each). |
Dec 13th
1962 |
78 kg |
   Enclosed
signals were recorded on 136.140 MHz in the time between
March 1964 and February 1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban. Enclosed
signals were recorded on 136.140 MHz in the time between
March 1964 and February 1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban.
|

|
Cosmos
12
KOSMOS 12
Zenit-2 #7
#00517
(1962-072A) |
Cosmos 12 was a Soviet
surveillance satellite launched from Baikonur aboard
a Vostok 2 rocket. It transmitted on 19.995 MHz. The
capsule was recovered after 8 days on December 30th
1962. |
Dec 22nd
1962 |
4730 kg |
 This
recording is part of vinyl no. 58 which was included
in the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The
man and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini This
recording is part of vinyl no. 58 which was included
in the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The
man and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini
|

|
Explorer
17
AE-A
S 6
#00564
(1963-0009A) |
Explorer 17 was a spin-stabilized
stainless-steel sphere 0.95 m in diameter. The spacecraft
was vacuum sealed in order to prevent contamination
of the local atmosphere. It measured neutral particle
density, neutral particle concentrations, and ion concentration
and electron temperature measurements. |
Apr. 3rd
1963 |
184 kg |
 This
recording is part of vinyl no. 57 which was included
in the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The
man and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini This
recording is part of vinyl no. 57 which was included
in the Italian Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The
man and the space) issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized
and kindly provided by Federico Manzini
|

|
TELSTAR
2
TELSTAR II
#00573
(1963-013A) |
Telstar 2, primarily
a communications satellite, carried an experiment designed
to measure the energetic proton and electron distribution
in the Van Allen belts. Telstar 2 differed from Telstar
1 by employing provisions for scientific information
to be transmitted in real time via the microwave telemetry
system so that telemetry could be obtained after the
2-yr timer had turned off the VHF beacon on 136.050
MHz (200 mW). The microwave tracking beacon was operating
at 4079.73 MHz (20 mW). The communication experiment
operated on 4169.72 MHz (2.25 W). |
May 7th
1963 |
176 kg |
 This recording
is from vinyl no. 59 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini. This recording
is from vinyl no. 59 which was included in the Italian
Enciclopaedia L置omo e lo spazio (The man and the space)
issued 1965 by Fratelli Fabbri. Digitized and kindly
provided by Federico Manzini.
|


|
LOFTI-2A
#00601
(1963-021B) |
The LOFTI
(Low Frequency Trans Ionospheric Satellite)
American earth magnetosphere satellites were launched
in 1961, 1962 and 1963. LOFTI attempted to determine
whether very low frequency (VLF) energy could penetrate
through the ionosphere and be received by submerged
submarines. The satellites demonstrated that under many
ionospheric conditions VLF signals were extremely attenuated
and could not be detected, making them unreliable for
submarine communication. LOFTI-2A was launched on a
Thor-DM21 Able-Star from Vandenberg AFB together with
Poppy2A (Solrad6), Poppy2B, Poppy2C (Radose) and Surcal3.
LOFTI-2A decayed on July 18th
1963. |
June
15th 1963 |
99
kg |
 Enclosed
signal was received by Bruce Window at Island Lagoon
Minitrack station (part of Honeysuckle Creek Tracking
Stations) and kindly provided by Colin Mackellar. Enclosed
signal was received by Bruce Window at Island Lagoon
Minitrack station (part of Honeysuckle Creek Tracking
Stations) and kindly provided by Colin Mackellar.
|

|
TIROS-7
TIROS-G
#00604
(1963-024A) |
 TIROS
7 (Television and InfraRed Observation Satellite) was
a spin-stabilized meteorological spacecraft designed
to test experimental television techniques and infrared
equipment. Signal received either on 136.234 MHz or
136.922 MHz in the time between March 1964 and February
1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban/South Africa. TIROS
7 (Television and InfraRed Observation Satellite) was
a spin-stabilized meteorological spacecraft designed
to test experimental television techniques and infrared
equipment. Signal received either on 136.234 MHz or
136.922 MHz in the time between March 1964 and February
1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban/South Africa.
|
June 19th
1963 |
135 kg |

|
RADOSE
Transit 5E1
SN39
#00671
(1963-038C) |
 RADOSE
also called Radiation Sat measured energetic charged
particles, magnetic fields, the solar spectrum, and
acquired geodetic data. It transmitted in 136, 162 and
324 MHz bands. The last data were transmitted during
November 1974. Recorded on July 2nd
1972 on 136.651 MHz by Greg Roberts. RADOSE
also called Radiation Sat measured energetic charged
particles, magnetic fields, the solar spectrum, and
acquired geodetic data. It transmitted in 136, 162 and
324 MHz bands. The last data were transmitted during
November 1974. Recorded on July 2nd
1972 on 136.651 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Sept 28th
1963 |
25 kg |
 Radose
recorded on Oct 24th 1973 on
136.651 MHz in CW/AM by Greg Roberts. Radose
recorded on Oct 24th 1973 on
136.651 MHz in CW/AM by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Relay 2
#00737
(1964-003A) |
 Relay
2 was primary a communications satellite but carried
also a particle experiment. Recorded in frequency band
136-138 MHz using an SSB receiver by Greg Roberts sometime
in the year 1974 or 1975. Relay
2 was primary a communications satellite but carried
also a particle experiment. Recorded in frequency band
136-138 MHz using an SSB receiver by Greg Roberts sometime
in the year 1974 or 1975.
|
Jan 21st
1964 |
184 kg |
 Relay
2 transmitted on two frequencies 136.140 MHz and 136.620
MHz. Multiple recordings were made on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. First recording was 136.620 MHz
in CW. Relay
2 transmitted on two frequencies 136.140 MHz and 136.620
MHz. Multiple recordings were made on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. First recording was 136.620 MHz
in CW.
|
 Second
recording was on 136.620 MHz in AM on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. Second
recording was on 136.620 MHz in AM on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
 Third
recording was on 136.140 MHz in CW on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. Third
recording was on 136.140 MHz in CW on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
 Fourth
recording was again recorded in CW on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. Fourth
recording was again recorded in CW on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
 Fifth
recording was recorded in FM on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. Fifth
recording was recorded in FM on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
 Sixth
recording was finally recorded in CW and AM on Oct 24th
1973 by Greg Roberts. Sixth
recording was finally recorded in CW and AM on Oct 24th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Echo 2
Echo C
#00740
(1964-004A) |
 Echo
2 was a 41-m balloon of aluminum foil-mylar laminate.
It decayed on June 7th 1969.
Its surface was used to reflect 162 MHz signals back
to Earth and thus act as a passive repeater. Echo 2
was the first joint space mission of the USA and of
the USSR. The Echo 2 beacon signal enclosed was recorded
either on 136.020 MHz or 136.170 MHz in various modes
in the time between March 1964 and February 1965 by
Greg Roberts in Durban. Echo
2 was a 41-m balloon of aluminum foil-mylar laminate.
It decayed on June 7th 1969.
Its surface was used to reflect 162 MHz signals back
to Earth and thus act as a passive repeater. Echo 2
was the first joint space mission of the USA and of
the USSR. The Echo 2 beacon signal enclosed was recorded
either on 136.020 MHz or 136.170 MHz in various modes
in the time between March 1964 and February 1965 by
Greg Roberts in Durban.
|
Jan 25th
1964 |
256 kg |

|
Ariel
2
S 52
S 52A
UK 2
UK-C
#00771
(1964-015A) |
 Ariel
2 carried 3 British experiments to measure galactic
radio noise. Echo 2 beacon recorded on 136.557 MHz in
the time between March 1964 and February 1965 by Greg
Roberts in Durban. Ariel
2 carried 3 British experiments to measure galactic
radio noise. Echo 2 beacon recorded on 136.557 MHz in
the time between March 1964 and February 1965 by Greg
Roberts in Durban.
|
Mar 27th
1964 |
68 kg |

|
Transit
5B-5
Transit O-2
OSCAR(NAV) 2
NNSS 30020
#00965
(1964-083D) |
TRansit 5B-5 is a radiation
satellite. It studied the magnetic field, celestial
field and collected ultraviolet data. This satellite
was still transmitting end of 2019 and is thus probably
the oldest satellite still transmitting. The sequence
of tones has speeded up quite considerably over time.
He transmits on 136.651 MHz in a SSB/FM multiplex mode. |
Dec. 13th
1964 |
60 kg |
 Transit
5B-5 recorded on Oct 24th 1973
on 136.50 MHz in AM/CW mixed by Greg Roberts. Transit
5B-5 recorded on Oct 24th 1973
on 136.50 MHz in AM/CW mixed by Greg Roberts.
|
  Signals
enclosed were recorded first in AM and then in FM mode.
Recorded on Dec 14th 1973 on
136.650 MHz by Greg Roberts. Signals
enclosed were recorded first in AM and then in FM mode.
Recorded on Dec 14th 1973 on
136.650 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
 The next
4 recording were made on June 19th
1999 on 136.650 MHz by Greg Roberts. He used a turnstile
antenna at about 10 meters above ground followed by
a low noise pre-amplifier with 20dB gain and about 1
dB noise figure. The first recording used the CW/SSB
mode of the receiver with a bandwidth of 2.4 kHz. The next
4 recording were made on June 19th
1999 on 136.650 MHz by Greg Roberts. He used a turnstile
antenna at about 10 meters above ground followed by
a low noise pre-amplifier with 20dB gain and about 1
dB noise figure. The first recording used the CW/SSB
mode of the receiver with a bandwidth of 2.4 kHz.
|
 The second
file was also recorded using the CW/SSB mode with 2.4
kHz bandwidth. Since the satellite signal is quite broad
(>30 kHz) one can easily hear several carriers when
using this mode of reception. The second
file was also recorded using the CW/SSB mode with 2.4
kHz bandwidth. Since the satellite signal is quite broad
(>30 kHz) one can easily hear several carriers when
using this mode of reception.
|
 Here
Greg Roberts used a narrower (0.8 kHz) bandwidth filter
to record the signal in CW/SSB mode. This bandwidth
is recommended for very faint satellites since it cuts
down the background noise. Here
Greg Roberts used a narrower (0.8 kHz) bandwidth filter
to record the signal in CW/SSB mode. This bandwidth
is recommended for very faint satellites since it cuts
down the background noise.
|
 This
signal was recorded using the FM detector of the receiver
with a bandwidth of approx. 25 to 30 kHz. Although the
FM modulation of Transit 5B-5 is very low, one can easily
hear the tones. Compare this to the CW/SSB recordings
and it should be very obvious why any serious radio
satellite tracker should have the capability of receiving
CW or SSB modes. FM is not suitable for weak signals.
Recorded by Greg Roberts. This
signal was recorded using the FM detector of the receiver
with a bandwidth of approx. 25 to 30 kHz. Although the
FM modulation of Transit 5B-5 is very low, one can easily
hear the tones. Compare this to the CW/SSB recordings
and it should be very obvious why any serious radio
satellite tracker should have the capability of receiving
CW or SSB modes. FM is not suitable for weak signals.
Recorded by Greg Roberts.
|
 More
than 46 years after its launch Transit 5B-5 was received
and recorded on March 26th
2011 at 11:07 UTC on 136.645 MHz in USB by Patrick Hajagos. More
than 46 years after its launch Transit 5B-5 was received
and recorded on March 26th
2011 at 11:07 UTC on 136.645 MHz in USB by Patrick Hajagos.
|
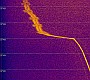 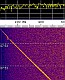  Transit
5B-5 was received on Dec. 30th
2012 at 07:45 UTC. The audio recording and also the
waterfall plot show interesting modulation and frequency
changes. Kindly provided by Flavio PY2ZX. Transit
5B-5 was received on Dec. 30th
2012 at 07:45 UTC. The audio recording and also the
waterfall plot show interesting modulation and frequency
changes. Kindly provided by Flavio PY2ZX.
|
 Almost
60 years its launch Transit 5B-5 was received and recorded
on August 27th 2024 at 18:32
UTC on 136.657 MHz in USB by Igor Monteiro PU4ELT. Recording
kindly provided by Igor PU4ELT. Please also have a look
at his website for other interesting recordings. Almost
60 years its launch Transit 5B-5 was received and recorded
on August 27th 2024 at 18:32
UTC on 136.657 MHz in USB by Igor Monteiro PU4ELT. Recording
kindly provided by Igor PU4ELT. Please also have a look
at his website for other interesting recordings.
|

|
LES-1
#01002
(1965-008C) |
LES- 1 (Lincoln Experimental
Satellite 1) is a US military communications satellite
launched from Cape Canaveral aboard a Titan 3A rocket.
LES-1 failed to reach Geostationary position when the
booster rockets failed leaving it in HEO. It was abandoned
in 1967. Besides the UHF telemetry transmitter it featured
also an X-band transmitter with 100mW output. More specifically
this was a beacon transmitting at 7740 MHz and a communications
transponder with an uplink at 8350 MHz and a downlink
at 7750 MHz. |
Feb
11th 1965 |
31
kg |
 Transmissions
of LES-1 were discovered 47 years after its launch by
Phil Williams in Cornwall/UK on Dec 18th
2012 and verified by other members of the #hearsat group.
The transmissions are not every day and seem to be linked
to extended periods of times when the satellite is in
sunlight. It seems that the transmissions are interrupted
by the availability of extended times when the satellite
is in sunlight. The satellite is evidently tumbling
as can be heard by the wobbling carrier with a time
constant of about 4.5 seconds. The signal is a single
un-modulated carrier on 236.997Mhz. The wobbling carrier
is clearly heard and can be seen also on enclosed spectrum
plot as is the slow normal Doppler shift associated
with its orbit. Transmissions
of LES-1 were discovered 47 years after its launch by
Phil Williams in Cornwall/UK on Dec 18th
2012 and verified by other members of the #hearsat group.
The transmissions are not every day and seem to be linked
to extended periods of times when the satellite is in
sunlight. It seems that the transmissions are interrupted
by the availability of extended times when the satellite
is in sunlight. The satellite is evidently tumbling
as can be heard by the wobbling carrier with a time
constant of about 4.5 seconds. The signal is a single
un-modulated carrier on 236.997Mhz. The wobbling carrier
is clearly heard and can be seen also on enclosed spectrum
plot as is the slow normal Doppler shift associated
with its orbit.  Enclosed
recording was made on Dec 19th
2012. AOS was at 12:00h UTC at a frequency of 236.998
Mhz whereas LOS was at 12:30h UTC at a frequency
of 236.992 MHz. Phil used a Create Log Periodic antenna
on an AZ/El mount, Enclosed
recording was made on Dec 19th
2012. AOS was at 12:00h UTC at a frequency of 236.998
Mhz whereas LOS was at 12:30h UTC at a frequency
of 236.992 MHz. Phil used a Create Log Periodic antenna
on an AZ/El mount,  an
LNA580 preamp by RfBay and an AOR AR5000 receiver with an SDR-IQ
connected at the IF output. The spectrum plot was generated
with Spectravue. Recording and spectrum plot kindly
provided by Phil Williams. an
LNA580 preamp by RfBay and an AOR AR5000 receiver with an SDR-IQ
connected at the IF output. The spectrum plot was generated
with Spectravue. Recording and spectrum plot kindly
provided by Phil Williams.
|
 Enclosed
signal of the wobbling carrier of LES-1 was received
and recorded on 236.998 MHz in USB on December 27th
2012 at 06:50 UTC by Matthias DD1US. Enclosed
signal of the wobbling carrier of LES-1 was received
and recorded on 236.998 MHz in USB on December 27th
2012 at 06:50 UTC by Matthias DD1US.
|
 Enclosed
spectrum plot of carrier of LES-1 shows that there are
2 time periods visible in the waterfall display: the
above mentioned 4 sec interval and a 30 sec interval.
Possibly the satellite is spinning (every 4 sec) and
rolling
end over end (every 30 sec). Received
and recorded on 236.99 MHz on January 4th
2013 at 11:50 UTC by Phil Williams. Enclosed
spectrum plot of carrier of LES-1 shows that there are
2 time periods visible in the waterfall display: the
above mentioned 4 sec interval and a 30 sec interval.
Possibly the satellite is spinning (every 4 sec) and
rolling
end over end (every 30 sec). Received
and recorded on 236.99 MHz on January 4th
2013 at 11:50 UTC by Phil Williams.
|
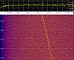  Enclosed
signal of LES-1 was received on December 22nd
2012 at 18:54 UTC. Recording and waterfall plot kindly
provided by Flavio PY2ZX. Enclosed
signal of LES-1 was received on December 22nd
2012 at 18:54 UTC. Recording and waterfall plot kindly
provided by Flavio PY2ZX.
|
 When
LES-1 goes in the Earth shadow the transmiter will stop
operating. When it gets out of the shadow it restarts
transmitting with periodic frequency jumps as can be
seen at the waterfall diagram enclosed. Received and
recorded on 236.99 MHz on January 19th
2013 at 03:04 UTC by Phil Williams. When
LES-1 goes in the Earth shadow the transmiter will stop
operating. When it gets out of the shadow it restarts
transmitting with periodic frequency jumps as can be
seen at the waterfall diagram enclosed. Received and
recorded on 236.99 MHz on January 19th
2013 at 03:04 UTC by Phil Williams.
|

|
Pegasus
1
#01085
(1965-009A) |
 Pegaus
1 transmitted on 136.440 MHz (1 W) a data and on 136.89
MHz (100 mW) a beacon signal. Beacon signal recorded
in February 1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban. Pegaus
1 transmitted on 136.440 MHz (1 W) a data and on 136.89
MHz (100 mW) a beacon signal. Beacon signal recorded
in February 1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban.
|
Feb 16th
1965 |
1452 kg |
 Pegasus
1 transmitted only as long as it was in sunlight. Recorded
on 136.890 MHz using an SSB receiver end of October
1974 by Greg Roberts. Pegasus
1 transmitted only as long as it was in sunlight. Recorded
on 136.890 MHz using an SSB receiver end of October
1974 by Greg Roberts.
|
 This
recording was done on October 29th
1974 by Greg Roberts. This
recording was done on October 29th
1974 by Greg Roberts.
|
|
GGSE-3
#01292
(1965-016C) |
 GGSE-3
(Gravity Gradient Stabilization Experiment 3) was a
small military satellite. Its design and deployment
techniques were later applied to the NOSS / Whitecloud
reconnaissance satellites. Recorded on 136.776 MHz in
March 1965 by Greg Roberts. GGSE-3
(Gravity Gradient Stabilization Experiment 3) was a
small military satellite. Its design and deployment
techniques were later applied to the NOSS / Whitecloud
reconnaissance satellites. Recorded on 136.776 MHz in
March 1965 by Greg Roberts.
|
Mar 9th
1965 |
4 kg |

|
SECOR 3
EGRS-3
#01208
(1965-016E) |
  SECOR
is an acronym for Sequential Correlation of Range and
is basically an electronic distance measuring system
in which four ground stations sequentially interrogate
a satellite-borne transponder. It was used by the US
Army Map service from 1964 onwards. Early satellites
transmitted on two carrier frequencies, namely 224.5
MHz and 449 MHz. Recorded first in AM and then in FM
on 136.840 MHz on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. SECOR
is an acronym for Sequential Correlation of Range and
is basically an electronic distance measuring system
in which four ground stations sequentially interrogate
a satellite-borne transponder. It was used by the US
Army Map service from 1964 onwards. Early satellites
transmitted on two carrier frequencies, namely 224.5
MHz and 449 MHz. Recorded first in AM and then in FM
on 136.840 MHz on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
Mar 9th
1965 |
18 kg |

|
SOLRAD
7B
GRAB 6
#01291
(1965-016D) |
 The US
satellite Solrad 7B was also called GRAB (Galactic Radiation
Experimental Background ) and was officially instrumented
to detect the solar X-ray emission. The US
satellite Solrad 7B was also called GRAB (Galactic Radiation
Experimental Background ) and was officially instrumented
to detect the solar X-ray emission.  The
first GRAB satellite was launched in 1960. However its
receivers were used to catalogue the waveforms and pulse
repetition frequencies of Soviet air defense radars.
The basic concept of operation is shown in the diagram
to the right. Recorded on 136.800 MHz in AM/FM by Mike
D. Kenny. The
first GRAB satellite was launched in 1960. However its
receivers were used to catalogue the waveforms and pulse
repetition frequencies of Soviet air defense radars.
The basic concept of operation is shown in the diagram
to the right. Recorded on 136.800 MHz in AM/FM by Mike
D. Kenny.
|
Mar
9th 1965 |
47
kg |
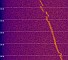 Enclosed
signal from Solrad-7B was received on Dec. 30th
2012 at 09:30 UTC. The waterfall plot shows interesting
jumps in the center frequency. Kindly provided by Flavio
PY2ZX. Enclosed
signal from Solrad-7B was received on Dec. 30th
2012 at 09:30 UTC. The waterfall plot shows interesting
jumps in the center frequency. Kindly provided by Flavio
PY2ZX.
|

|
Beacon
C
(Explorer 27)
#01328
(1965-032A) |
 Explorer
27 was also called Beacon C and investigated the ionosphere.
It transmitted on 136.740 MHz. Recorded June 7th
1975 in CW by Greg Roberts. Explorer
27 was also called Beacon C and investigated the ionosphere.
It transmitted on 136.740 MHz. Recorded June 7th
1975 in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
Apr
29th 1965 |
60
kg |
 Recorded
June 7th 1975 in FM by Greg
Roberts. Recorded
June 7th 1975 in FM by Greg
Roberts.
|
 Recorded
June 7th 1975 in FM by Greg
Roberts. Recorded
June 7th 1975 in FM by Greg
Roberts.
|
 Recorded
May 17th 1972 on 136.740 MHz
by Greg Roberts. Recorded
May 17th 1972 on 136.740 MHz
by Greg Roberts.
|
 Explorer
27 recorded on Oct 24th 1973
on 136.740 MHz in AM mode by Greg Roberts. Explorer
27 recorded on Oct 24th 1973
on 136.740 MHz in AM mode by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Pegasus
2
#01381
(1965-039A) |
 Pegasus
2 was a huge scientific satellite for the observation
of meteorites. It transmitted on 136.410 MHz (data)
and 136.890 MHz (telemetry and tracking beacon). Recorded
on October 15th 1973 in AM
most likely on 136.890 MHz by Greg Roberts. Pegasus
2 was a huge scientific satellite for the observation
of meteorites. It transmitted on 136.410 MHz (data)
and 136.890 MHz (telemetry and tracking beacon). Recorded
on October 15th 1973 in AM
most likely on 136.890 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
May 25th
1965 |
10500 kg |
 Pegasus
2 CW transmission increased suddenly whenever the satellite
entered the shadow of the Earth. This can be heard nicely
on this recording in CW mode on October 24th
1973 by Greg Roberts. Pegasus
2 CW transmission increased suddenly whenever the satellite
entered the shadow of the Earth. This can be heard nicely
on this recording in CW mode on October 24th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|


|
TIROS-10
OT 1
#01430
(1965-051A) |
Tiros-10 (Television
and InfraRed Observation Satellite) is
a sun-synchronous meteorological spacecraft designed
to
develop improved capabilities for obtaining and using
TV
cloud-cover pictures from satellites and operated as
an
interim operational satellite. The spin-stabilized spacecraft
is in the form of an 18-sided right prism, 107 cm
across opposite corners and 56 cm high, with a reinforced
baseplate carrying most of the subsystems and a cover
assembly (hat). Electrial power is supplied to the spacecraft
by approximately 9000 1- by 2-cm silicon solar cells
that were mounted on the cover assembly and by 21 nickel-cadmium
batteries. A single monopole antenna for reception
of ground commands extends from the top of the
cover assembly. A pair of crossed-dipole telemetry antennas
(235 MHz) project down and diagonally out from the
baseplate.
TIROS-10
features an advanced vidicon camera system (AVCS).
AVCS (television) transmission was at 235 MHz with
2 W output power.
TIROS-10
transmits tracking signals with 50 mW on 136.230
(increased over lifetime to 136.235 MHz) and 136.920
MHz.
TIROS-10 features an advanced vidicon camera
system (AVCS). AVCS (television) transmission was at
235 MHz with 2 W output power.
TIROS-10 transmits
tracking signals with 50 mW on 136.230 (increased over
lifetime to 136.235 MHz) and 136.920 MHz. |
July 2nd
1965 |
127 kg |
 TIROS-10
transmitted a continuous tone on both frequencies, 136.230
and 136.920 MHz, recorded on Oct. 24th
1973 in CW and AM by Greg Roberts. TIROS-10
transmitted a continuous tone on both frequencies, 136.230
and 136.920 MHz, recorded on Oct. 24th
1973 in CW and AM by Greg Roberts.
|
 Recording
made on Dec 14th 1973 on 136.230
MHz by Greg Roberts. Recording
made on Dec 14th 1973 on 136.230
MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
 Recording
made on Dec 14th 1973 on 136.920
MHz by Greg Roberts. Recording
made on Dec 14th 1973 on 136.920
MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
 Recording
made on Dec 14th 1973 on unknown
frequency by Greg Roberts. Recording
made on Dec 14th 1973 on unknown
frequency by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Pegasus 3
Saturn
SA-10
#01467
(1965-060A) |
 In its
stored position with panels folded inside the Apollo
service module Pegasus 3 was 5.3 m high, 2.1 m wide,
and only 28 cm deep. The spacecraft was equipped with
appendages like wings which extended to form a huge
plane 29.3 m long and 4.3 m wide. Pegasus 3 transmitted
on 136.410 MHz (data) and 136.890 MHz (telemetry and
tracking beacon) and sounded like the previous 2 Pegasus
satellites. This signal is probably the beacon on 136.89
MHz and was recorded in the time between March 1964
and February 1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban. In its
stored position with panels folded inside the Apollo
service module Pegasus 3 was 5.3 m high, 2.1 m wide,
and only 28 cm deep. The spacecraft was equipped with
appendages like wings which extended to form a huge
plane 29.3 m long and 4.3 m wide. Pegasus 3 transmitted
on 136.410 MHz (data) and 136.890 MHz (telemetry and
tracking beacon) and sounded like the previous 2 Pegasus
satellites. This signal is probably the beacon on 136.89
MHz and was recorded in the time between March 1964
and February 1965 by Greg Roberts in Durban.
|
Jul 30th
1965 |
1452 kg |

|
GEOS 1
GEOS A
Explorer 29
#01726
(1965-089A) |
 GEOS
1 (Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite) was a gravity-gradient-stabilized,
solar-cell powered satellite targeted for geodetic studies..
Recorded on 136.83 MHz in the time between November
1965 and Spring 1966 by Greg Roberts in Durban. GEOS
1 (Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite) was a gravity-gradient-stabilized,
solar-cell powered satellite targeted for geodetic studies..
Recorded on 136.83 MHz in the time between November
1965 and Spring 1966 by Greg Roberts in Durban.
|
Nov 6th
1965 |
387 kg |


|
Alouette-2
Alouette-B
#01804
(1965-098A) |
Alouette 1 was a Canadian
small ionospheric observatory instrumented with a sweep
frequency ionospheric sounder, a VLF receiver, an energetic
particle experiment, a cosmic noise experiment and a
electrostatic probe. The spacecraft used two long dipole
antennas (73 m and 22.8 m long). Alouette-2 had a tracking
beacons transmitting with 50 mWatts on 136.980 MHz and
two telemetry transmitter on 136.080 MHz (2 Watts) and
136.590 MHz (0.25 Watts).Routine operations were terminated
in July 1975. The spacecraft was successfully reactivated
on November 28th and 29th
1975 in order to obtain data on its 10th
anniversary. |
Nov.
29th 1965 |
147
kg |
In August
2013, 48 years after its launch, signals from Alouette-2
were jointly rediscovered by Raydel Abreu Espinet CM2ESP
in Cuba and Mike Kenny in Australia. All 3 transmitters
could be detected. The detected signals were:
 136.590
MHz : a variable strength stable carrier with weak intermittent
sidebands at approx. +/- 3.5, 5.0 and 13.5 kHz 136.590
MHz : a variable strength stable carrier with weak intermittent
sidebands at approx. +/- 3.5, 5.0 and 13.5 kHz
 136.080
MHz : a variable strength unstable carrier 4 to 5 kHz
below nominal frequency and weaker intermittent unstable
sidebands at +/- 20 to 23 kHz from the carrier 136.080
MHz : a variable strength unstable carrier 4 to 5 kHz
below nominal frequency and weaker intermittent unstable
sidebands at +/- 20 to 23 kHz from the carrier
 136.980
MHz : a strong stable carrier only 136.980
MHz : a strong stable carrier only
Signals were received in SSB on October
3rd 2013 at 23:10 UTC by Raydel
CM2ESP in Havanna/Cuba. Raydel used a horizontal Moxon
antenna fixed pointed to Zenith and a RTL-SDR Dongle
with a 35dB preamplifier. Recordings kindly provided
by Raydel CM2ESP. |

|
ESSA 2
OT 2
#02091
(1966-016A) |
 ESSA
2 was a meteorological satellite providing real-time
earth cloud-cover TV pictures for use in weather analysis
and forecasting. It transmitted telemetry on 136.500
MHz and a tracking beacon signal on 136.770 MHz. Recorded
on 136.770 MHz in spring 1966 by Greg Roberts in Durban. ESSA
2 was a meteorological satellite providing real-time
earth cloud-cover TV pictures for use in weather analysis
and forecasting. It transmitted telemetry on 136.500
MHz and a tracking beacon signal on 136.770 MHz. Recorded
on 136.770 MHz in spring 1966 by Greg Roberts in Durban.
|
Feb 28th
1966 |
286 kg |

|
COSMOS 114
Zenit-4
#02133
(1966-028A) |
 2nd
Generation high resolution Soviet Photo Reconnaissance
satellite. 2nd
Generation high resolution Soviet Photo Reconnaissance
satellite.
This FSK-PDM signal was recorded on 19.995
MHz on April 8th 1966 by Sven
Grahn.
|
Apr 6th
1966 |
4730 kg |

|
SECOR 7
EGRS-7
#02411
(1966-077B) |
 EGRS-7
was a similar type satellite to the SECOR satellites
using the same telemetry format. Frequency was 136.800
MHz. Recorded on Dec 14th 1973
by Greg Roberts. EGRS-7
was a similar type satellite to the SECOR satellites
using the same telemetry format. Frequency was 136.800
MHz. Recorded on Dec 14th 1973
by Greg Roberts.
|
Aug 19th
1966 |
17 kg |
 EGRS-7
was recorded on Oct 24th 1973
in AM mode by Greg Roberts. EGRS-7
was recorded on Oct 24th 1973
in AM mode by Greg Roberts.
|
 SECOR-7
was received on Dec. 31st 2012
at 10:16 UTC. Waterfall plot kindly provided by Flavio
PY2ZX. SECOR-7
was received on Dec. 31st 2012
at 10:16 UTC. Waterfall plot kindly provided by Flavio
PY2ZX.
|

|
ERS 15
#02412
(1966-077C) |
 ERS (Environmental
Research Satellite) was an Air force technology satellite
also known as Octahedron Research Satellite (ORS-1).
Was launched together with and ejected by MIDAS-11 (1966-077A).
Recorded on 137.800 MHz using an SSB receiver by Greg
Roberts. ERS (Environmental
Research Satellite) was an Air force technology satellite
also known as Octahedron Research Satellite (ORS-1).
Was launched together with and ejected by MIDAS-11 (1966-077A).
Recorded on 137.800 MHz using an SSB receiver by Greg
Roberts.
|
Aug 19th
1966 |
4.5 kg |

|
SECOR 8
EGRS-8
#02520
(1966-089B) |
  The SECOR
(Sequential Correlation of Range) series of satellites
were used for US Military mapping purposes. Recorded
first in SSB and then in AM on 136.830 MHz on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts. The SECOR
(Sequential Correlation of Range) series of satellites
were used for US Military mapping purposes. Recorded
first in SSB and then in AM on 136.830 MHz on Dec 14th
1973 by Greg Roberts.
|
Oct 5th
1966 |
17 kg |
 Recorded
on May 17th 1972 on 136.830
MHz by Greg Roberts. Recorded
on May 17th 1972 on 136.830
MHz by Greg Roberts.
|

|
Intelsat
2F-1
Atlantic 1
Canary Bird
Intelsat 2A
Lanny Bird 2F1
#02514
(1966-096A) |
 Commercial
Communication Satellite of COMSAT Corporation. Did not
reach final orbit due to a failure in the apogee motor.
However was still used to transmit live television and
other communications traffic. Used 2 redundant repeaters
with 125 MHz bandwidth supporting 240 two-way telephone
circuits or one TV channel. Telemetry system used two
encoders, two VHF transmitters, eight whip antennas
as well as a 4 GHz beacon. The beacon signals were transmitted
continuously and modulated with telemetry signals. Recorded
in frequency band 136-138 MHz using an SSB receiver
by Greg Roberts. Commercial
Communication Satellite of COMSAT Corporation. Did not
reach final orbit due to a failure in the apogee motor.
However was still used to transmit live television and
other communications traffic. Used 2 redundant repeaters
with 125 MHz bandwidth supporting 240 two-way telephone
circuits or one TV channel. Telemetry system used two
encoders, two VHF transmitters, eight whip antennas
as well as a 4 GHz beacon. The beacon signals were transmitted
continuously and modulated with telemetry signals. Recorded
in frequency band 136-138 MHz using an SSB receiver
by Greg Roberts.
|
Oct
26th 1966 |
355
kg |
 Recorded
on Aug 2nd 1972 in CW by Greg
Roberts. Recorded
on Aug 2nd 1972 in CW by Greg
Roberts.
|
  Intelsat
2F-1 stranded in an elliptical 3360 x 37038 km orbit.
Recorded twice on October 24th
1973 on 136.440 MHz in CW by Greg Roberts. Intelsat
2F-1 stranded in an elliptical 3360 x 37038 km orbit.
Recorded twice on October 24th
1973 on 136.440 MHz in CW by Greg Roberts.
|
 Recorded
in excellent quality on September 2nd
1975 on 136.440 MHz by Greg Roberts. Recorded
in excellent quality on September 2nd
1975 on 136.440 MHz by Greg Roberts.
|

|
OV1-9
FARO 1
Manifold
#02610
(1966-111A) |
 OV1-9
performed radiation bio-hazard experiments. Recorded
on August 2nd 1972 on 136.620
MHz by Greg Roberts. OV1-9
performed radiation bio-hazard experiments. Recorded
on August 2nd 1972 on 136.620
MHz by Greg Roberts.
|
Dec 11th
1966 |
104 kg |
Picture |
Object
name
#NORAD |
Description |
Launch
Date |
Weight |